|
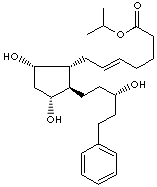
LATANOPROST |
| Isopropyl (Z)-7-((1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-2-((3R)-3-hydroxy-5-phenylpentyl)cyclopentyl)-5- heptenoate; Xalatan; Isopropyl (5Z,9alpha,11alpha,15R)-9,11,15-trihydroxy-17-phenyl- 18,19,20- trinor-prost-5-en-1-oate; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
130209-82-4 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C26H40O5 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
432.59 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Prostaglandin analogue / Antiglaucoma |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
clear to pale yellow viscous oil |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
(Freely soluble in DMSO, soluble in methanol) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health Hazard: 4, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Highly toxic by ingestion |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be fatal if swallowed. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
22-36/37-61 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Latanoprost is a prescription medication used for reducing eye pressure.
Specifically, it is used to lower eye pressure in people with open angle
glaucoma or ocular hypertension to help prevent damage to the optic nerve.
Latanoprost comes in the form of an eye drop that is generally used once daily.
Common side effects include changes in eye color, blurred vision, and eyelash
and eyelid changes. http://eyes.emedtv.com/latanoprost/latanoprost.html
The fundamental rationale for treating glaucoma is that abnormal IOP plays a major role in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Although high IOP is certainly not the only factor contributing to ON damage, it is one of the few risk factors that can be clinically modified. Medically lowering IOP in patients with OH may reduce the incidence of glaucoma.134 In at least two-thirds of patients with high-tension glaucoma, marked lowering of the IOP stops progression of the disease. Even in NTG patients, the level of the IOP is a risk factor related to the degree of glaucomatous damage. (http://www.aoa.org/) Topical beta blockers are the standard first-line agents, most commonly
timolol (Timoptic). Newer beta blockers include betaxolol (Betoptic),
levobunolol (Betagan), carteolol (Ocupress), and metipranolol (OptiPranolol).
Timolol has been used for years, and these agents are well tolerated.
Pharmacological Actions
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to slightly yellowish powder |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass Test A (HPLC),B (IR) |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% ~ 102.0% |
|
WATER |
0.5% max |
| SOLVENT RESIDUE |
Ethanol 1.0% max |
|
ISOMERS |
15(S)-cis
isomer: 0.1% max |
|
TOTAL IMPURITY |
1.0% max |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+32° ~ +38° |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|