|
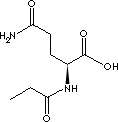
GLYCYLGLUTAMINE MONOHYDRATE |
| Gly-gln monohydrate; N2-Glycyl-L-glutamine monohydrate; Glycyl-L-glutamine; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
13115-71-4 (anhydrous); 172669-64-6 (monohydrate) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C7H13N3O4·H2O |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
221.21 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Dipeptide |
| RELATED CATEGORIES | Neuropeptide |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
|
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
|
| POLYMERIZATION |
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
This substance is not classified as dangerous |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. In case of eye contact, flush eyes with water as a precaution. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. In case of skin contact, wash off with soap and plenty of water. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Glutamine (Gln) is the most abundant free amino acid in the body and plays a vital role in amino acid transport and nitrogen balance. Gln is also a primary fuel for rapidly dividing cells such as enterocytes and lymphocytes, which protect mucosa barricade and enhance immune functions[1]. Patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery usually have malnutrition and Gln concentration is low in blood due to several factors: mechanical obstruction, limitation of food intake, tumor-induced cachexia, obstruction of pancreaticobiliary, malabsorption and ongoing blood loss. Moreover, intravascular and free muscle glutamine pools become depleted in response to perioperative abrosia and operative stress. Free Gln is lack of stability in solution and intravenous adminitration is limited. Glutamine dipeptide (L-alanyl-L-glutamine) can be taken via vein and hydrolyzed into glutamine in circulation as Gln substitution. It was given to patients undergoing abdominal surgery in order to improve their postoperative nitrogen balance and immunonutrition[2]. Therefore, it is worth knowing whether routine supplementation of glutamine dipeptide in parenteral nutrition (PN) can amend clinical outcomes. Meta-analysis has been applied in medical research to improve statistical effi ciency, to evaluate the disadvantage of established studies and to draw reliable conclusions from various potentially relevant studies. It is the most promising approach for future research and a guideline for clinical treatment[3]. This meta-analysis aims to enhance our understanding of the clinical and economical validity of glutamine dipeptide for patients undergoing abdominal surgery. (http://www.wjgnet.com/) The objective of this research is to test the hypothesis that glycyl- L-glutamine, a dipeptide synthesized through the post-translational processing of Beta-endorphin, acts as a neurotransmitter in brain and a circulating hormone in the periphery. To test this hypothesis, we established three working objectives: (1) to evaluate the physiological responses produced by glycyl L glutamine and test whether it modulates the opiate actions of Beta-endorphin; (2) to examine its distribution in brain and pituitary and determine whether it is specifically co-localized with Beta-endorphin; (3) to characterize the receptors which mediate glycyl L glutamine's pharmacologic effects. During the current project period, we found that glycyl L glutamine produces three markedly different pharmacologic responses: it stimulates a trophic response in cardiac myocytes, inducing expression of the asymmetric form of acetylcholinesterase, a classical marker for synaptic innervation; it produces neuroimmune regulatory effects in T lymphocytes, enhancing c-myc oncogene expression. (http://oai.dtic.mil/)Glycyl-glutamine (Gly-Gln) is an inhibitory dipeptide synthesized from β-endorphin1–31. Previously, we showed that Gly-Gln inhibits morphine conditioned place preference, tolerance, dependence and withdrawal. In this study, we tested whether Gly-Gln's inhibitory activity extends to other rewarding drugs, specifically nicotine. Rats were conditioned with nicotine (0.6 mg/kg, s.c.) for four days and tested on day five. Glycyl-glutamine (100 nmol i.c.v.) inhibited acquisition and expression of a nicotine place preference significantly. Cyclo(Gly-Gln) (100 nmol i.c.v. or 25 mg/kg i.p.), a cyclic Gly-Gln derivative, blocked expression of nicotine place preference but Gly-D-Gln (100 nmol i.c.v.) was ineffective. To study nicotine withdrawal, rats were treated with nicotine (9 mg/kg/day) for seven days and conditioned place aversion was induced with mecamylamine (1 mg/kg, s.c.). Glycyl-glutamine blocked acquisition of place aversion to mecamylamine but not U50,488, a kappa opioid receptor agonist. Glycyl-glutamine thus inhibits the rewarding effects of nicotine and attenuates withdrawal in nicotine dependent rats. (http://farmakoloji.uludag.edu.tr/) |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
CONTENT |
99.0% min |
| RELATED SUBSTANCES |
Cyclo(Gly-Gln): 0.5% max L-Pyroglutamic Acid: 0.5% max Individual impurity: 0.5% max Total impurity: 1.0% max |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
-7.0° ~ -9.0° |
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
| CHLORIDE | 0,2% max |
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|