|
Angiotensin is a polypeptide vasopressor hormone formed by the catalytic action
of renin which is released mainly by the kidneys in response to low blood volume
or low sodium content in the body. The juxtaglomerular cells release renin, when
juxtaglomerular apparatus decreases in the kidneys. Renin (called
angiotensinogenase, EC 3.4.23.15) is an enzyme of the hydrolase class that
catalyzes cleavage of the leucine-leucine bond in angiotensinogen (a serum
globulin) to generate angiotensin I (decapeptide hormone) in the liver. Among
angiotensin I's various biological activity, it acts mainly as a precursor to
angiotensin II (octapeptide hormone) which is a vasopressor and stimulator of
aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex, and functions also as a
neurotransmitter. A. II is formed by catalytic action of the hydrolase called
peptidyl-dipeptidase A (EC 3.4.15.1) on C-terminal oligopeptide (A.I). In case
of the cleavage of A. I to the activated A.II, it is called
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE); in case of the cleavage and inactivation of
kinins, it is called kininase II (also called dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I).
Angiotensin III (heptapeptide) is a degradation product of A. II, having less
vasopressor activity than the parent compound. The renin-angiotensin system
plays an important role in the regulation of blood volume and blood pressure,
stimulates antidiuretic hormone and aldosterone production, and the hypothalamus
to activate the thirst reflex, but is crucial in the pathogenesis of
hypertension patients due to blood vessels constrict, retention of fluid and
raising blood pressure. ACE inhibitors prevent A.I from converting into A.II.
and act to widen the blood vessels and make it easier for the heart to pump
blood through the body. If high blood pressure continues for a long time, it
may damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in
heart attack, heart failure, or kidney failure. ACE inhibitors are used in ther
treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure, and to alleviate strain on
hearts damaged as a result of a heart attack. They prevent from cardiovascular
disorders, left ventricular dysfunction, and nephropathy in diabetes mellitus.
They also helps control the amount of blood in your body. Angiotensin
receptor blockers (ARBs) reduce hypertension by displacing A.II 2 from receptors
on the surface of cells. There are A.I receptor as well as A.II receptor. They
are used when patients are intolerant of ACE inhibitor therapy. They have fewer
side effects.
Angiotensin-Converting enzyme Inhibitors
- Benazepril
(CAS #: 86541-75-5)
- Captopril
(CAS #: 62571-86-2)
- Enalapril
(CAS #: 75847-73-3)
- Fosinopril
(CAS #: 98048-97-6)
- Imidapril
(CAS #: 89371-37-9)
- Lisinopril
(CAS #: 83915-83-7)
- Moexipril
(CAS #: 103775-10-6)
- Quinapril
(CAS #: 85441-61-8)
- Perindopril (CAS
#: 82834-16-0)
- Ramipril
(CAS #: 87333-19-5)
- Trandolapril
(CAS #: 87679-37-6)
Angiotension II Receptor Blockers
- Candesartan
(CAS #: 145040-37-5)
- Eprosartan
(CAS #: 133040-01-4)
- Irbesartan
(CAS #: 138402-11-6)
- Losartan
(CAS #: 114798-26-4)
- Olmesartan
(CAS #: 144689-24-7)
- Telmisartan
(CAS #: 144701-48-4)
- Valsartan
(CAS #: 137862-53-4)
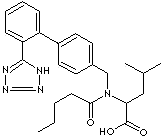
Valsartan is a nonpeptide angiotensin II blocker used as an antihypertensive. It
is a white crystalline powder; melting point 116 - 117 C; slightly soluble in
water, soluble in alcohol; administered orally.. Chemical designation is
N-(1-Oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl] methyl]-L-valine.
|