| CAS
NO. |
20893-30-5 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
244-104-6 |
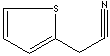
| FORMULA |
C6H5SN |
| MOL
WT. |
123.17 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2934.90 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral
rat LD50: 87mg/kg
|
| SYNONYMS |
2-Cyanomethylthiophene;
2-(Cyanomethyl)thiophene; |
| Thien-2-ylacetonitrile; Thiophene-2-acetonitrile;
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Dark yellow to
brown liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
-5
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
234
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.157 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
slightly soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
4.25 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
> 110 C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Thiophene, also known as thiofuran, is a cyclic compound containing four carbon
atoms and one sulfur atom in the ring. Thiophene is an analog to furan and pyrrole where the sulfur
atom is replaced by O and NH
respectively. Thiophene is a toxic, flammable, and colorless liquid; insoluble in water (soluble in most
organic solvents including alcohol and
ether); melting at -38 C, boiling at 84 C. Thiophene is the simplest aromatic
compound containing sulfur atom and it shares some similar
chemical properties with benzene. The lone electron pairs on sulfur in the delocalized pi electron system does
not exhibits the properties of thioethers but aromaticity.
The sulfur atom is unreactive but the adjacent carbons
are susceptible to attack
by electrophiles. It is reactive toward sulfonation. In commercial thiophene
can be prepared by the reaction of butane and sulfur.
Thiophenes are also prepared by the reaction of diketones with Lawesson's
reagent. Thiophene and its derivatives exist in petroleum or coal. Thiophene derivatives
are also found in natural plant pigments. Biotin, a water-soluble B-complex vitamin,
is a reduced thiophene derivative. Thiophene moiety
is found in ccphalothin antiboitics. Thiophene is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Its
derivatives are used in manufacturing dyes, aroma compounds and
pharmaceuticals. They are used as monomers to make
condensation copolymers. Organic conductive polymers are responsible for the
important materials science for the application of polymer
electro
luminescence. 2-Thiopheneacetonitrile
is used as an intermediate of antibiotics;
Cefoxtin, Cephaloridine,
Cephalothin. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Dark yellow to
brown liquid |
|
ASSAY
|
95.0%
min
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
200kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1
(Packing Group: III) |
| UN
NO. |
2810 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
European Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/21/22, Safety Phrases: 23 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF NITRILE
|
|
Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-.
Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium
cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN
are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in
many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
|
|
PRICE
INFORMATION
|
|

|
