|
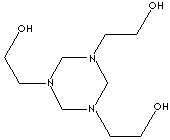
Hexahydro-1,3,5-tris(hydroxyethyl)-s-triazine;
Trishydroxyethyl-hexahydro-s-triazine;
1,3,5-tris(2-hydroxyethyl)hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine;
1,3,5-Triazine-1,3,5(2H,4H,6H)-triethanol; s-Triazine-1,3,5(2h,4h,6h)triethanol;
Grotan;
|
|
Triazine is the chemical species of six-membered heterocyclic ring compound with
three nitrogens replacing carbon-hydrogen units in the benzene ring structure.
The names of the three isomers indicate which of the carbon-hydrogen units on
the benzene ring position of the molecule have been replaced by nitrogens,
called 1,2,3-triazine, 1,2,4-triazine, and 1,3,5-triazine respectively.
Symmetrical 1,3,5-triazine is the common. Triazines are prepared from
2-azidocyclopropene through thermal rearrangement (1,2,3-triazine), from
1,2-dicarbonyl compound with amidrazone by condensation reaction
(1,2,4-triazine) and from cyanic acid amide by trimerization (1,3,5-triazine).
Pyridine is the aromatic nitrogen heterocycle compound having only one nitrogen,
and diazines are with 2 nitrogen atoms and tetrazines are with 4 nitrogen atoms
on the benzene ring system. Triazines are weak base. Triazines have much weaker
resonance energy than benzene, so nucleophilic substitution is preferred than
electrophilic substitution. Triazines are basic structure of herbicides,
examples are amitole (CAS #: 61-82-5), atrazine (CAS #: 1912-24-9), cyanazine
(CAS #: 21725-46-2), simazine (CAS #: 122-34-9), trietazine (CAS #: 1912-26-1).
Large volume of triazines are used in the manufacture of resin modifiers such
as melamine and benzoguanamine. Melamine (1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine) is
reacted with formaldehyde to from a very durable thermoset resin. Benzoguanamine
(2,4-Diamino-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine) is used to increase thermoset properties
of alkyd, acrylic and formaldehyde resins. Triazines are also useful as
chromophore groups in colorants and Chlorine attached in Triazine compounds
undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions well with with hydroxyl groups in
cellulose fibres. Some triazine family compounds are used in pharmaceutical
industry as coupling agent for the synthesis of peptide in solid phase as well
as solution and as side chain of antibiotics. Triazine compounds are used in
formulating bactericide and fungicide. They are used as preservatives in oil
field applications. They are used as disinfectant, industrial deodorant and
biocide in water treatment. They are used as a bleaching agents. Triazinetriethanol,
an analogue of cyanuric acid
(1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triol)
is used in formulating bactericide and fungicide. It
is used a low toxicity biocide particularly in the wet
state. End products can include adhesives, industrial
cleaning systems, polymer emulsions, and paint.
|