| CAS
NO. |
90-15-3 |
|
| ELINCS/EINECS
NO. |
201-969-4 |
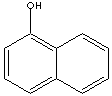
| FORMULA |
C10H7OH |
| MOL
WT. |
144.17 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2907.15 |
| TOXICITY |
Oral
rat LD50: 1870 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
1-Naphthol;
1-Naphthalenol;
C.I. 76605; |
| 1-Hydroxynaphthalene;
Durafur developer D; Fouramine ern; Fourrine 99; Fourrine
ern; Furro ER; Nako TRB; Oxidation base 33; |
| SMILES |
1-Naphthalenesulfonic
acid with Caustic Alkali
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
BETA-NAPHTHOL
|
| CAS
NO. |
135-19-3 |
|
| ELINCS/EINECS
NO. |
205-182-7 |
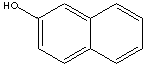
| FORMULA |
C10H7OH |
| MOL
WT. |
144.17 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2907.15 |
| TOXICITY |
Oral
rat LD50: 1960 mg/Kg |
| SYNONYMS |
2-Naphthol;
2-Hydroxynaphthalene;
2-Naphthalenol; |
| Isonaphthol;
Beta-hydroxynaphthalene; Hydroxynaphthalene;
Naphthalenol; Naphthyl alcohol; Naphthyl hydroxide;
|
| SMILES |
2-Naphthalenesulfonic
acid with Caustic soda
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
|
ALPHA-NAPHTHOL |
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White
to tan crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
95
- 96 C
|
| BOILING
POINT |
278
- 280 C
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.20
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Very
slightly soluble |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION
|
450
C
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
4.5
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
2 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 Contact
Rating: 3 (Corrosive) |
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
125
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
BETA-NAPHTHOL
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White
to yellow crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
121
- 122 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
285
- 286 C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.22 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly
soluble |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION
|
550
C
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
4.97 |
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 |
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
153
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions (Discolors may occur
on exposure to light.) |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
|
|
Naphthols are either of two crystalline monohydric alcohols, derived from
naphthalene and belong to the phenol family. There are position isomers;
alpha-naphthol (also called 1-naphthol) is 1-hydroxynaphthalene and
beta-naphthol (also called 2-naphthol) is 2-hydroxynaphthalene. The compound
1-naphthol is made by heating 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid with caustic alkali or
by heating 1-naphthylamine with water under pressure. The compound 2-naphthol is
manufactured by fusing 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid with caustic soda. The
different positions provide various chemical structures which offer important
roles to each characteristic colours. Naphthols are slightly soluble in water
but readily soluble in short alcohols, ethers chlorinated solvents, and caustic
alkalis. They are used directly in making several dyes and are converted into
numerous corresponding amines, esters, ethers and carboxylic derivatives as well
as into numerous sulfo- and nitro-group substituted (mono-, di- and tri) naphthol
compounds. They find extensive applications in making dyes, pigments,
fluorescent whiteners, tanning
agents, antioxidants, and antiseptics. Naphthol structure is found as a ligand
in transition-metal catalysts particularly in the form of
binaphthol (binol) which is composed of two naphthol rings connected at one
carbon site on each ring. Optically active binol is widely used in asymmetric
synthesis of rearrangements, epoxidations, reductions. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
ALPHA-NAPHTHOL |
|
APPEARANCE
|
White
to yellowish flakes or crystalline
powder |
| CONTENT |
99.0%
min
|
| ISOMER
IMPURITY |
0.2%
max
|
| MELTING
POINT |
93
C min
|
| MOISTURE |
0.1%
max
|
|
BETA-NAPHTHOL
|
|
APPEARANCE
|
White
to yellowish flakes or crystalline
powder |
| CONTENT |
99.0%
min
|
| ISOMER
IMPURITY |
0.2%
max
|
| MELTING
POINT |
120
C min
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
|
ALPHA-NAPHTHOL |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in bag |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
8
|
| UN
NO. |
1759
|
|
BETA-NAPHTHOL
|
| PACKING |
25kgs
in bag |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| REMARKS |
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 21/22/37/38/41,
Safety Phrases:22/26/37/39 (ALPHA-NAPH
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/22, Safety
Phrases:24/25 (BETA-NAPHTHOL)
|

