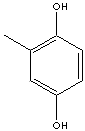
| METHYLHYDROQUINONE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 95-71-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-443-7 | |
| FORMULA | CH3C6H3(OH)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 124.14 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
|
|
|
TOXICITY |
Oral mouse LD50: >400 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 2-methyl-1,4-benzenediol; Toluhydroquinone; | |
| 2,5-Dihydroxytoluene; 2-Methylhydroquinone; Methyl-p-hydroquinone; 2,5-toluenediol; P-toluquinol; Tolylhydroquinone; 2-Methylhydrochinon (German); 2-Metilhidroquinona (Spanish); 2-Methylhydroquinone (French); | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystal | |
|
MELTING POINT |
125 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.34 | |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1, Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
455 C | |
| FLASH POINT |
172 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| It is used as a stabilizer for unsaturated polyesters and as an antioxidant for fatty esters, linseed oil, and other nonfood fats and oils.. It is used as a stabilizer to inhibit peroxide formation in ethers, chlorinated hydrocarbons and ethyl cellulose. It is also used as an intermediate to manufacture other stabilizers, dyes, pharmaceuticals and plasticizers. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystal | |
| ASSAY |
99.0% min | |
|
ASH |
0.01% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 2811 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF QUINONE | ||
|
Quinone is a group of aromatic compounds containing two opposite carbonyl groups (C=O) and the other two pairs of carbon atoms linked by vinylene group(-CH=CH) in a six-membered unsaturated ring. The carbonyl groups are located in different rings and form various chemical structures which offer important roles to colours. Quinones are used in photography and dye manufacture. Quinones occur benzoquinones, naphthoquinones, anthraquinones, and polycyclic quinones. Though quinones are found in plants and in a few animals, they usually are prepared by oxidation of aromatic amines, polyhydric phenols, and polynuclear hydrocarbons.The reduction of quinone to the corresponding dihydroxy form is an important characteristic reaction. In acidic solution, p-benzoquinone is reduced reversibly to hydroquinone. The so-called quinhydrone electrode, containing equimolar solution of quinone and hydroquinone, is used to determine hydrogen ion concentrations depends on the oxidation-reduction reactions. Hydroquinone and its derivatives used principally in photographic dye chemicals, in medicine, as an antioxidant, and in paints, varnishes, and motor fuels and oils. Hydroquinone and certain derivatives are also used as polymerization inhibitors by direct reacting with peroxy-free radical to tie up free radicals. |
||