PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
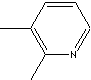
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.945
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Picoline :
Three structural isomers of methyl pyridines (alpha, beta, gamma-
positions)
Lutidine : Six structural isomers of dimethyl pyridines (2,3-,
,24-, 2,5-, 2,6-, 3,4-, 3,5- positions)
Collidine : Three structural isomers
of trimethyl pyridines (2,3,5-, 2,3,6-, 2,4,6- positions)
Pyrimidine:
Pyridine alteration containing nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and
3
Piperidine: Hexahydropyridine (saturated form)
Nicotinic acid:
pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
Pyridine and its derivatives are very important in industrial field as well as in bio chemistry. Nucleotide consist of either a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine). Three major pyrimidines in living systems are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Pyrimidine and its derivatives are biologically important components of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. Some pyridine system is active in the metabolism in the body. Certain nitrogenous plant products also have pyridine class compounds. They can be the parent compound of many drugs, including the barbiturates. Pyridine and its derivatives are used as solvents and starting material for the synthesis of target compounds such as insecticides, herbicides, medicines, vitamins, food flavorings, feed additives, dyes, rubber chemicals, explosives, disinfectants, and adhesives. Pyridine is also used as a denaturant for antifreeze mixtures, as a dyeing assistant in textiles and in fungicides.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
MOISTURE
Amidines and guanidines, the compound NH=C(NH2)2, are strongly basic reagents. Bases activation of deprotonation is the first step in the synthesis. The strength of basicity, nucleophilicity, steric hindrance or solubility are the factors to select reagents for the best results in the chemical reactions such as alkylation, tautomerization, dehydrohalogenation, michael-addition, esterification, saponification, acylation, silylations, aldol-condensation, eliminations, and cyclization. The order of basicity strength of some amines are; TBD > MTBD > DBU > DBN > TMG > Quinuclidine > TMP, Pempidine > Triethylamine > TED > Tributylamine > Collidine > Lutidine
- TBD: 1,5,7-Triazabicyclo(4.4.0)dec-5-ene; 1,3,4,6,7,8-Hexahydro-2H-pyrimido[1,2-a] pyrimidine, CAS #: 5807-14-7
- MTBD :7-Methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo(4.4.0)dec-5-ene;1,3,4,6,7,8-Hexahydro-1- methyl-2H-pyrimido [1,2-a]pyrimidine, CAS #: 84030-20-6
- DBU: 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene; 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-Octahydropyrimidol[1,2-a] azepine, CAS #: 6674-22-2
- DBN: 1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene, CAS #: 3001-72-7
- TMG: 1,1,3,3-Tetramethylguanidine; N,N,N',N'-Tetramethylguanidine, CAS #: 80-70-6
- Quinuclidine: 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, CAS #: 100-76-5
- TMP: 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine, CAS #: 768-66-1
- Pempidine: 1,2,2,6,6-Pentamethylpiperidine, CAS #: 79-55-0
- TED: 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan; Triethylenediamine, CAS #: 280-57-9
- Collidine: Trimethylpyridine, CAS #: 108-75-8 (2,4,6- Isomer)
- Lutidine: Dimethylpyridine, CAS #: 108-48-5 (2,6- Isomer)
|
Product |
CAS RN |
|
2,4-Lutidine |
108-47-4 |
|
2,6-Lutidine |
108-48-5 |
|
2,3-Lutidine |
583-61-9 |
|
3,4-Lutidine |
583-58-4 |
|
2,5-Lutidine |
589-93-5 |
|
3,5-Lutidine |
591-22-0 |
| 2,6-Lutidine N-oxide | 1073-23-0 |
| 3,5-Diacetyl-1,4-dihydrolutidine | 1079-95-4 |
| 2,4-Dimethylpyridine 1-oxide | 1122-45-8 |
| 2-Ethyl-3,5-dimethylpyridine | 1123-96-2 |
| 2-Ethyl-4,6-dimethylpyridine | 1124-35-2 |
| Etidin | 1149-23-1 |
| 3,5-Dicarbethoxy-2,6-dimethyl-4-ethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine | 1153-66-8 |
|
Diethyl 4-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-lutidine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
1165-06-6 |
| 6-Ethyl-2,3-dimethylpyridine | 1463-01-0 |
| Clopidol | 2971-90-6 |
|
2,6-Bis(chloromethyl)pyridine |
3099-28-3 |
| 2,6-Dimethylpyridine borane | 3999-42-6 |
| 4-Nitro-2,6-lutidine-1-oxide | 4808-64-4 |
|
2-Amino-4,6-dimethylpyridine |
5407-87-4 |
| 4-((4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)-2,6-lutidine 1-oxide | 7349-99-7 |
| 3,5-Dimethyl-4-nitropyridine 1-oxide | 14248-66-9 |
| Bis(2,4-dimethylpyridinio)dichlorocuprate(II) | 14434-99-2 |
|
3-Nitro-2,6-lutidine |
15513-52-7 |
| Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 17438-14-1 |
| 4-((p-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)-3,5-lutidine 1-oxide | 19456-77-0 |
| 4-((p-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)-2,5-lutidine 1-oxide | 19471-27-3 |
| 3,5-Diacetyl-1,4-dihydro-4-phenyl-2,6-lutidine | 20970-67-6 |
| Diethyl 4-(4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine- 3,5- dicarboxylate | 21203-88-3 |
| 1-Benzyl-1,2-dihydro-2-((4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-3,4-dimethylpyridine | 22185-50-8 |
| 3-Ethyl-2,6-dimethylpyridine | 23580-52-1 |
| 1-Benzyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-2-((4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-3,4-dimethylpyridine | 23909-52-6 |
| Dimethylpyridine | 27175-64-0 |
| Bis(benzyl) 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 36138-79-1 |
| Pentacarbonyl(2,6-dimethylpyridine)tungsten | 36252-39-8 |
| Didodecyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 36265-41-5 |
| 2-(p-Aminobenzamido)-4,6-dimethylpyridine | 36845-10-0 |
| 6-(p-Aminobenzamido)-2,3-dimethylpyridine | 36845-12-2 |
| 3-(p-Aminobenzamido)-2,6-dimethylpyridine | 36987-32-3 |
|
4-Nitro-2,3-lutidine-N-oxide |
37699-43-7 |
| N-(2-Chloro-1-naphthylidene)-3-amino-2,6-lutidine | 38641-70-2 |
| 2,6-Lutidine-alpha2,3-diol | 42097-42-7 |
| 3-Ethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydro-2,4-dimethylpyridine | 52199-37-8 |
| N-Octyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 53242-40-3 |
| 3,4-Dimethyl-2-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl)pyridine | 57330-96-8 |
| cis-Dichloro(3,5-dimethylpyridine)(ethene)platinum | 66841-93-8 |
| Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate | 67035-22-7 |
| cis-Bis(3,5-dimethylpyridine)dichloroplatinum | 73289-27-7 |
| 2-(2-Diethylaminoethoxy)-4,6-dimethylpyridine hydrochloride | 74195-91-8 |
| Methyl 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine- 3,5-dicarboxylate | 74687-14-2 |
| N-Hexadecyl-2,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 78191-89-6 |
| N-Decyl-3,5-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-56-9 |
| N-Dodecyl-2,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-51-4 |
| N-Dodecyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-45-6 |
| N-Decyl-2,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-50-3 |
| N-Hexadecyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-47-8 |
| N-Hexyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-43-4 |
| N-Hexyl-3,5-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-54-7 |
| N-Octyl-2,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-49-0 |
| N-Decyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-44-5 |
| N-Tetradecyl-2,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-52-5 |
| N-Tetradecyl-3,4-dimethyl pyridinium iodide | 88477-46-7 |
|
2-Amino-5-bromo-4,6-dimethylpyridine |
89856-44-0 |
| cis-Dichlorobis(3,5-dimethylpyridine)platinum | 91602-67-4 |
| 3-N-(Methylbenzym)carbamoyl-5-propionyl-2,6-lutidine | 92751-45-6 |
| Bis(tert-butyl) 4-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 94266-08-7 |
| tert-Butyl ethyl 4-butyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 94266-04-3 |
| Diethyl 4-butyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 94266-06-5 |
| tert-Butyl ethyl 4-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 94266-03-2 |
| Lutidinium 6-ethyl-1,2,4,2H-thiadiazine-3,5(4H,6H)-dione 1,1-dioxide | 96434-10-5 |
| 4-(alpha-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)benzyl)-2,6-lutidine | 101737-54-6 |
| 3,4-Dimethylpyridine adenine dinucleotide | 102686-21-5 |
| 4-Nonyl-3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine | 144883-73-8 |
| 4-Dodecyl-3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine | 144883-74-9 |