|
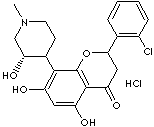
ALVOCIDIB HCl |
|
(−)-2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(3S,4R)-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-piperidinyl]-4H-1- benzopyran- 4-one hydrochloride; Alvocidib; Flavopiridol hydrochloride; cis-(-)-2-(2-Chlorophenyl)- 5,7-dihydroxy- 8-(3-hydroxy- 1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
146426-40-6, 131740-09-5 (HCl) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C21H20ClNO5·HCl |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
438.30 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
2mg/ml (Soluble in DMSO) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. Nitrogen oxides. Hydrogen chloride gas |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Harmful. Do not breathe dust. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD CODE |
XN |
|
RISK STATEMENTS |
22 |
|
SAFETY STATEMENTS |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | |
|
Alvocidib; A synthetic
N-methylpiperidinyl chlorophenyl flavone compound. As an inhibitor of
cyclin-dependent kinase, alvocidib induces cell cycle arrest by preventing
phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and by down-regulating cyclin
D1 and D3 expression, resulting in G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. This
agent is also a competitive inhibitor of adenosine triphosphate activity. Check
for active
clinical trials or closed
clinical trials using this agent. (NCI
Thesaurus) (http://www.cancer.gov/)
Flavopiridol is effective in inducing cell cycle arrest and cytotoxicity in rhabdoid tumors. Its effects are correlated with the down-regulation of cyclin D1 and the up-regulation of p21. Flavopiridol is potentially a novel chemotherapeutic agent for rhabdoid tumors. (http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/) In general, pharmacological inhibitors of CDKs display selective anti-proliferative effects on cycling cells, especially tumor cells. Depending on the selectivity profile, growth arrest in G0/G1 (CDK4/6-selective) or in G1/S and G2/M (pan-CDK- and CDK1/2-selective) is observed. More importantly, many compounds, especially potent CDK2 inhibitors, have been observed to induce apoptosis selectively in transformed cells [62]. As discussed above, many compounds with very high potency against CDKs in vitro are available. However, in many cases this biochemical potency does not translate into cellular potency, presumably due to unknown mechanistic reasons and perhaps because of high physiological ATP concentrations. Connected with this problem is the question of what are the actual cellular targets of a biochemical CDK inhibitor. One technique that has been applied to CDK inhibitors is affinity chromatography of cell lysates on immobilized inhibitor preparations. Indeed it was found that, apart from CDKs, other proteins were also bound. (http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |