PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
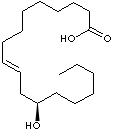
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
5.5 C
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
224 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
8 max
Fatty Acids are aliphatic carboxylic acid with varying hydrocarbon lengths at one end of the chain joined to terminal carboxyl (-COOH) group at the other end. The general formula is R-(CH2)n-COOH. Fatty acids are predominantly unbranched and those with even numbers of carbon atoms between 12 and 22 carbons long react with glycerol to form lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Fatty acids all have common names respectively lilk lauric (C12), MyrIstic (C14), palmitic (C16), stearic (C18), oleic (C18, unsaturated), and linoleic (C18, polyunsaturated) acids. The saturated fatty acids have no solid bonds, while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid has one solid bond (also described as olefinic) and polyunsaturated fatty acids like linolenic acid contain two or more solid bonds. Lauric acid (also called Dodecanoic acid) is the main acid in coconut oil (45 - 50 percent) and palm kernel oil (45 - 55 percent). Nutmeg butter is rich in myristic acid (also called Tetradecanoic acid ) which constitutes 60-75 percent of the fatty-acid content. Palmitic acid(also called Hexadecylic acid ) constitutes between 20 and 30 percent of most animal fats and is also an important constituent of most vegetable fats (35 - 45 percent of palm oil). Saturated carboxylic acids (C1 – C10) are liquids whereas long chain saturated fatty acids are solids. The long carbon chains form compact pile in a regular pattern with high van der waals attractions resulting in high melting points. If solid bonds are present in the fatty acid portion of the molecule, the fat is said to be unsaturated. Monounsaturated contains only one solid bond; polyunsaturated contains more than one solid bonds (up to an maximum of about six) which are never conjugated and can form geometric cis/trans isomers. Naturally occuring unsaturated fatty acids are liquids as they are in the cis- geometrical configuration which twists molecular structure (the kink of the cis form); can not pack closely, lowers melting points. Unsaturated fatty acids in the kinked, cis form are much more common in cells than the trans form continues in the same direction without a pronounced kink. The cis form of unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid at biological temperatures and are more abundant in living organisms. Fatty acids are named by the number of carbon atoms n and the number of solid bonds m as (n:m). The system for naming solid bond position is to indicate the first solid bond in the carbon backbone counting from the opposite end from the carboxyl group. The terminal carbon atom is called the omega carbon atom. The term "omega-3 or omega-6" signifies that their single solid bond is occured at carbon number 3 or 6 respectively counted from and including the omega carbon. Human bodies are not capable of synthesizing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids which are called essential fatty acids must be obtained through the diet. (These fatty acids were designated as "Vitamin F", until it was realized that they must be classified with the fats.) Fatty acids are converted to enegy through the process called fatty acid oxidation in liver cells. Fatty acids are used as basic building blocks of biological membranes, for long-term energy storage (the major components of triglycerides) as well as for the precursors of eicosanoid hormones.
|
COMMON NAME |
SYSTEMATIC NAME |
CAS RN |
SYMBOL |
| Myristolenic Acid |
(Z)-9-Tetradecenoic Acid |
544-64-9 |
14:1 n-5 |
| Palmitoleic Acid | (Z)-9-Hexadecenoic Acid | 373-49-9 |
16:1 n-7 |
| Palmitelaidic Acid | (E)-9-Hexadecenoic Acid | 10030-73-6 |
16;1 n-7 (trans) |
| Vaccenic Acid | (Z)-11-Octadecenoic Acid | 506-17-2 | 18:1 n-7 |
|
Oleic Acid |
(Z)-9-Octadecenoic Acid |
112-80-1 | 18:1 n-9 |
| Elaidic Acid | (E)-9-Octadecenoic Acid | 112-79-8 | 18:1 n-9 (trans) |
| Linoelaidicic Acid | (E,E)-9,12-Octadecadienoic Acid | 506-21-8 |
18:2 n-6 (trans) |
| Linoleic Acid | (Z,Z)-9,12-Octadecadienoic Acid | 60-33-3 |
18:2 n-6 |
| Isolinoleic Acid | (E,E)-9,11-Octadecadienoic Acid | 544-71-8 |
18:2 n-6 (trans) |
| Linolenic Acid | (Z,Z,Z)-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic Acid | 463-40-1 | 18:3 n-3 |
| gamma -Linolenic Acid | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic Acid | 506-26-3 | 18:3 n-6 |
|
Moroctic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12,15-Octadecatetraenoic Acid |
20290-75-9 |
18:4 n-3 |
| Eicosenoic Acid |
(Z)-11-Ecosenoic Acid |
5561-99-9 | 20:1 n-9 |
| Eicosadienoic Acid |
(Z,Z,)-11,14-Ecosadienoic Acid |
2091-39-6 | 20:2 n-6 |
| Mead Acid |
(Z,Z,Z)-5,8,11-Eicosatrienoic Acid |
20590-32-3 | 20:3 n-9 |
|
Eicosatrienoic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z)-11,14,17-Eicosatrienoic Acid |
17046-59-2 |
20:3 n-3 |
| Dihomo-g -Linolenic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic Acid |
1783-84-2 | 20:3 n-6 |
| Omega-3 Arachidonic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14,17-Eicosatetraenoic Acid |
24880-40-8 | 20:4 n-3 |
| Arachidonic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z)-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic Acid |
506-32-1 | 20:4 n-6 |
| Timnodonic Acid | (Z,Z,Z,Z,Z)-5,8,11,14,17-Eicosapentaenoic Acid | 10417-94-4 | 20:5 n-3 |
| Erucic Acid |
(Z)-13-Docosenoic Acid |
112-86-7 |
22:1 n-9 |
| Docosadienoic Acid |
(Z,Z)-13,16-Docosadienoic Acid |
17735-98-7 |
22:2 n-6 |
| Docosatrienoic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z)-13,16,19-Docosatrienoic Acid |
28845-86-5 |
22:3 n-3 |
| Adrenic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z)-7,10-13-16-Ocosatetraenoic Acid |
28874-58-0 |
22:4 n-6 |
| Docosapentaenoic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z,Z)-4,7,10,13,16-Docosapentaenoic Acid |
25182-74-5 |
22:5 n-6 |
| Docosapentaenoic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z,Z)-7,10,13,16,19-Docosapentaenoic Acid |
24880-45-3 |
22:5 n-3 |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid |
(Z,Z,Z,Z,Z,Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic Acid |
6217-54-5 |
22:6 n-3 |
| Nervonic Acid |
(Z)-15-Tetracosaenoic Acid |
506-37-6 | 24:1 n-9 |
| Tetracosahexaenoic Acid |
((Z,Z,Z,Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12,15,18,21-Tetracosahexaenoic Acid |
24:6 n-3 |