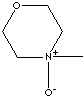| CAS
NO. |
7529-22-8, 70187-32-5 |
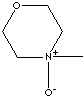
|
| EINECS
NO. |
231-391-8 |
| FORMULA |
C5H11NO2·H2O |
| MOL
WT. |
135.16 |
| H.S.
CODE |
|
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
4-Methylmorpholine 4-oxide monohydrate;
|
|
4-Methylmorpholine-N-oxide; 4-Methylmorpholine N-oxide monohydrate; NMO monohydrate;
4-Methylmorpholin-4-oxidmonohydrat
(German); 4-Oxido de 4-metilmorfolina,
monohidrato (Spanish); 4-Oxyde de 4-méthylmorpholine, monohydrate (French);
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to light beige powder
|
| MELTING
POINT |
69
- 74 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.13 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
| Improver of transition-metal complex catalytic oxygenation of both alkenes (or
alkanes) and oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to light beige powder
|
| ASSAY |
97.0%
min
|
| ASH |
0.1%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kg
in fiber drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases:
26-37/39 |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF
MORPHOLINE |
Morpholine is a hygroscopic, weak basic, oily and volatile liquid; with a
characteristic amine odor; melting point -5 C, boiling point at 129 C; miscible
with water and with many alcohol organic solvents such methanol, ethanol,
acetone, ethers, BTX (it is used as a solvent itself), but has limited
solubility in alkaline solutions. It decomposes on heating resulting toxic
nitrogen oxides and violently reacts with strong oxidants resulting fire hazard
and attacking copper and its compounds. It can be prepared by the reductive
ammonation of diethylene glycol with hydrogen, by the dehydration of
diethanolamine with a strong acid (oleum) and by heating bis(chloroethyl)ether
with excess ammonia. It is a cyclic amino ether as well as a secondary amine.
1,4-Dioxane is the form which nitrogen atom is replaced by oxygen. The ether
property of morpholine is typically inert. The secondary amine property
involves in the most chemical reactions. Morpholine is a versatile chemical. It is
used as a solvent itself for resins, dyes, and waxes. Its alkyl derivatives
(e.g. N-methylmorpholine, N-ethylmorpholine) are used as a catalyst for the
production of polyurethane foams. Nitrogen in ring system involves in the introduction
of sterically demanding asymmetric center to achieve
effective stereocontrol. Morpholine has a similar volatility with water.
It is used as a pH adjustment additive in fossil fuel and steam systems as
a corrosion inhibitor. The most important use is as a chemical intermediate to
prepare below compounds:
- Rubber
chemicals for vulcanization and stabilization
- Corrosion
inhibitors in boiler water treatment system and in aqueous hydraulic liquids to
protect metals against corrosion and tarnish by acid fumes.
- Optical
brighteners which are stable to chlorine bleaches for the use in detergent
formulations
- Fatty acid
salts for the formulation of water-resistant emulsifier or plasticizer in
toiletry and cosmetic products.
- Sulfonamide
bactericides or disinfectants
- Quaternary
morpholinium salts for hair conditioners and deodorant products
- Colourants
for hair dyes and blueprints
- Pharmaceuticals
(analgesics, local anaesthetics, antibiotics, antimycotics and for
anti-plaques)
|