METHYL BENZOATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
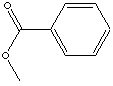
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
82 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Methyl benzoate
PubChem Compound Summary - Methyl benzoate
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Methyl benzoate
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Methyl benzoate
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Methyl benzoate
http://courses.chem.psu.edu/
The
ester group is an important functional group that can be synthesized
in a number of different ways. The low-molecular-weight esters have
very pleasant odors and indeed are the major components of the flavor
and odor aspects of a number of fruits. Although the natural flavor
may contain nearly a hundred different compounds, single esters
approximate the natural odors and are often used in the food industry
for artificial flavors and fragrances (see table below). ��In snapdragon
flowers, the volatile ester methyl benzoate is the most abundant
scent compound. It is synthesized by and emitted from only the upper
and lower lobes of petals, where pollinators (bumblebees) come in
contact with the flower. Emission of methyl benzoate occurs in a
rhythmic manner, with maximum emission during the day, which correlates
with pollinator activity.�� (Taken from http://www.plantcell.org/cgi/content/abstract/13/10/2333)
In this experiment, you will be synthesizing methyl benzoate via
Fischer esterification.
Local:
APPLICATION:
Solvent for cellulose esters ,
Dying carrier, Disinfectant additive, Penetrating agent,
Pesticides
APPEARANCE
90.0% min ( or 96.0% min or 99.0% min)
MOISTURE
0.5% max
0.1% max
25 max
Benzoic acid, a white, crystalline organic compound, is a family carboxylic acids. It has a carboxyl group bound directly to a benzene ring. Though it occurs naturally in some plants, It is commercially manufactured by the reaction of toluene with oxygen at temperatures around 200 C in the presence of cobalt and manganese salts as catalysts. Pure benzoic acid melts at 122 C and is very slightly soluble in water. It is widely used as a food preservative, normally as the sodium, potassium, or calcium salts and their derivatives especially in acid foods. Benzoate preservatives applications in foods, drugs and personal products are well established. It is also widely as an intermediate for chemicals, alkyd resins, polyesters, plasticizers, dyestuffs, preservatives, and rubber activators and retardants. Benzoic Acid is a diverting agent in crude oil recovery applications.
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician
P280
Wear eye protection/face protection
P501 Dispose of contents/container through a waste management company authorized
by the local government.
![]()
RISK PHRASES
22
SAFETY PHRASES