PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
31685-59-3 (hydrochloride)
928-72-3 (dihydrochloride)
U$15.00/kg CFR by sea
for 200kgs
U$80/kg CFR by air
for 10kgs
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Imide is a compound derived from ammonia, in which two atoms of hydrogen have been replaced by a bivalent acid group or two monovalent acid groups. Imide compounds contain the divalent radical -CONHCO-. Frequently, the term of imide refers to the combined forms such as maleimides, phthalimides, and succinimides. The radical =NH is called imido group. Imido is a prefix used to denote the presence in a compound of the bivalent group =NH attached to only acid radicals. Imine is a compound containing the bivalent =NH group combined with a bivalent nonacid group, as R-HC=NH. It is produced by the condensation reactions of aldehydes or ketones with ammonia (or amines). Imino is a prefix denoting the presence of the bivalent group =NH attached to nonacid radicals. Iminodiacetic Acid which has nitrogen atoms and short chain carboxylic groups is used as an intermediate for the manufacture of chelating agents, glyphosate herbicides, surfactants. Its salts and esters are used in manufacturing pesticides.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
MELTING POINT
240 C min
MOISTURE
0.5% max
ASH
|
Product |
CAS RN |
| (4-Iodoacetanilido)iminodiacetic acid | 5502-61-4 |
| 4,4'-Bis(alpha-iminodiacetic acid)azotoluene | 80462-88-0 |
| 4,5,6,7-Tetrabromo-2-cresolphthalein-3'-methyliminodiacetic acid | 85563-15-1 |
| 4-Ethoxy-ida | 63245-29-4 |
| Dimethyl ((3-acetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzyl)imino)diacetate | 19014-73-4 |
| N-(2,4,6-Triiodo-3-acetamidobenzyl)iminodiacetic acid hemihydrate | 19014-74-5 |
| N-(2,4,6-Triiodo-3-aminobenzyl)iminodiacetic acid | 19014-76-7 |
| Nitroiminodiacetic acid | 25081-33-8 |
| 2,2'-(Nitrosoimino)bisacetonitrile | 16339-18-7 |
| N-(2-Acetamido)iminodiacetic acid disodium salt |
41689-31-0 |
| N-(2-Acetamido)iminodiacetic acid sodium salt |
7415-22-7 |
| (S)-N-(5-Amino-1-carboxypentyl)iminodiacetic acid |
113231-05-3 |
| N-(5-Amino-1-carboxypentyl)iminodiacetic acid |
160369-83-5 |
| Bis(diaminoethyl ether)-N,N,N'N'-tetraacetic acid | 923-73-9 |
| Bromo-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)carbamoylmethyl iminodiacetic acid | 132170-00-4 |
| Bromo-N-(2,6-isopropylphenyl)carbamoylmethyl iminodiacetic acid | 132169-99-4 |
| Calcein Blue | 54375-47-2 |
| Catechol-3,6-bis(methyleneiminodiacetic acid) | 82773-07-7 |
| Chlorhexidine acetate | 56-95-1 |
| Chloro(1,2-diaminocyclohexane)(N-methyliminodiacetato)platinum(IV) | 145482-83-3 |
| Cobalt iminodiacetate | 13869-30-2 |
| Copper(II)-iminodiacetate | 14219-31-9 |
| Dichloro-(3-(methyleneiminodiacetic acid)phenyl-(2',3'-diamino propion amide))platinum(II) | 110947-34-7 |
| Dichloro-(4-hydroxy-3-(methyleneiminodiacetic acid)phenyl-(2',3'-diamino propionamide)) platinum(II) | 110988-41-5 |
| Dichloro-(4-methyleneiminodiacetic acid)phenyl-(2',3'-diaminopropion amide)platinum(II) | 110947-38-1 |
| Diethyl iminodiacetate | 6290-05-7 |
| Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate dihydrate | 6381-92-6 |
|
Disodium N-(2-hydroxyethyl)iminodiacetate |
135-37-5 |
| Edetate disodium | 139-33-3 |
| Edetate Tetrasodium | 64-02-8 |
| Edetic acid | 60-00-4 |
| 2-Iminoethanethiol diacetate | 101221-41-4 |
| Etifenin | 63245-28-3 |
| Diethyl iminodiacetate | 6290-05-7 |
| Lauroyliminodiacetic acid | 3775-51-7 |
| Lauroyliminodiacetic acid disodium salt | 18426-54-5 |
| N-Benzyliminodiacetic acid mono-3-phenyl-4-methylanilide | 101626-78-2 |
| Iminodiacetic acid-ruthenium (III) complex | 117676-57-0 |
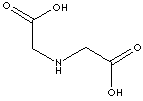
| Iminodiacetic acid | 142-73-4 |
| Iminodiacetic acid disodium Salt | 928-72-3 |
| Iminodiacetic acid monosodium | 32607-00-4 |
| Iminodiacetonitrile | 628-87-5 |
| Lidocaine iminodiacetic acid | 62605-94-1 |
| Lidofenin | 59160-29-1 |
| Mercury(II), iminodiacetato- | 18728-32-0 |
|
N-(2,6-Diisopropylphenylcarbamoylmethyl)iminodiacetic acid |
65717-97-7 |
| N-(2-Acetamido)iminodiacetic acid | 26239-55-4 |
|
N-(2-Carboxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid |
6245-75-6 |
| N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid | 93-62-9 |
| N-(3-Bromo-2,4,6-trimethylphenylcarbamoylmethyl)iminodiacetic acid | 78266-06-5 |
| N-(Carboxymethyl)-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine | 5994-61-6 |
|
N-[2-(Carboxymethylthio)ethyl]iminodiacetic acid monohydrate |
81877-53-4 |
|
N-Boc-iminodiacetic acid |
56074-20-5 |
| N-Decyliminodiacetato-1,2-diaminocyclohexane-platinum(II) | 107241-37-2 |
|
N-Fmoc-iminodiacetic acid |
112918-82-8 |
| N-Formyliminodiacetic acid | 71449-79-1 |
| Nickel iminodiacetate | 13869-33-5 |
| N-Methyliminodiacetato-1,2-diaminocyclohexane platinum(II) | 96322-12-2 |
| N-Nitrosoiminodiacetic acid | 25081-31-6 |
| N-Phenyliminodiacetic acid anhydride | 1137-73-1 |
| Sodium iminodiacetate monohydrate | 31685-59-3 |
|
Sodium iminodiacetate dibasic hydrate |
207398-95-6 |
|
Sodium iminodiacetate dibasic monohydrate |
17593-73-6 |
| Strombine | 4408-64-4 |
| Dibutyltin hydroxyethyliminodiacetic acid | 68239-46-3 |