PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
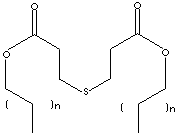
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
Thiodipropionate, Antioxidant, Stabilizer
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Didodecyl 3,3-thiodipropionate is used as a secondary stabilizer and antioxidant in combination with phenolic antioxidant for polymers (ABS, polypropylene, polyethylene and polyesters). It is approved to use in food packaging. It is also used stabilizer in oils, lubricants, sealants, and adhesives.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/
Mechanisms of antioxidant action: the nature of the
redox behaviour of thiodipropionate esters in polypropylene
http://www.epa.gov/
....DLTDP,
DTTDP and DSTDP are all produced by reacting the same intermediate,
thiodipropionitrile (TDPN), with different fatty alcohols. DLTDP
uses lauryl alcohol, DTTDP uses iso-tridecyl alcohol and DSTDP uses
stearyl alcohol. The reaction of TDPN with the alcohols is an esterification
using acid catalysts (hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid). Water
is removed under vacuum to drive the esterification to completion.
Then the catalyst is neutralized and salts and impurities removed
in a series of filtrations and washes. The molten DLTDP and DSTDP
are converted to solid products by flaking and packaged. The liquid
DTTDP product is drummed. The TDPN intermediate is made by reacting
acrylonitrile and sodium sulfhydrate in aqueous solution. The resulting
aqueous phase is split off, the product phase washed with water
and the remaining TDPN used to make the thioesters. The reactions
all take place in enclosed reactors, thus limiting potential worker
exposure. The DLTDP, DTTDP and DSTDP all have very low vapor pressures
at ambient temperatures so the risk of vapor contact during manufacture
and drumming is relatively low. These chemicals are used by our
customers who add them to variety of plastics such as polyethylene,
polyolefins (mostly polypropylene), and polystyrene. Common use
levels of DLTDP and DSTDP are 0.1 to 0.2 %. The polymers are then
further processed into items such as washing machine agitators,
battery cases, food packaging materials, and household appliances.
.....
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
97.0% min
SET POINT
COLOR, APHA
60 max
VOLATILE MATTER
0.5% max (at 100 C for 2 hrs)
0.1 max (mg KOH/kg)
ASH CONTENT
0.01% max
Not regulated
OTHER INFORMATION