PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
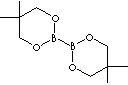
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white powder
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
REFREACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Suzuki reaction is an efficient, cost effective and environment-friendly methodology for the selective carbon-carbon couplings of organoboranes ( organic boronic acids, boronate esters and diboron esters) to (aryl, benzyl, or vinyl) halides, diazonium salts or trifaltes in the presence of a transition-metal catalyst (particularly palladium catalysts) and in a basic solution which is necessary to neutralize the liberated acid. The mechanism is similar to that of Heck reaction. Suzuki coupling reactions undergo under milder condition than Heck reactions. The Suzuki reaction permit the use of cyano-, ester-, carbonyl-, and nitro aryl rings. The Suzuki reaction is preferred in the pharmaceutical synthesis due to non-toxicity of boron species. Examples of palladium catalysts are;
- Bis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium [CAS #: 32005-36-0]
- Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) [CAS #: 14221-01-3]
- Hexakis(µ-acetato)tripalladium(II) [Trimer of Palladium(II) acetate] [CAS #: 3375-31-3]
Triflate, trifluoromethanesulfonate, is one of the strongest acids known as a super acid. Substituted trifluoroborates are alternatives to boronic acids in C-C bond forming (rhodium catalyzed) and Suzuki reactions. These salts are stable in air and water. They are excellent leaving groups. They ususally don't require to add either additional ligands or base for cross coupling. Whereas they do not form cyclic anhydrides which boronic acids readily.
APPEARANCE
white powder
98.0% min
180 - 185 C