PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
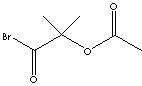
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
REFREACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
97.0% min
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ACYL HALIDES
|
|
|
| 2-ACETOXY-2-METHYLPROPIONYL BROMIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO | 40635-67-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | ||
| FORMULA | C6H9BrO3 | |
| MOL WT. | 209.04 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2918.90 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 2-(Acetyloxy)-2-methyl-Propanoyl Bromide; | |
| alpha-Acetoxy-isobutyryl Bromide; 1-Bromocarbonyl-1-methylethyl acetate; | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.43 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Decomposes | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFREACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| 2-Acetoxy-2-methylpropionyl Bromide is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes and other organic chemicals. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to light yellow liquid | |
| ASSAY |
97.0% min | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs, 240kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 1760 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 14-34-37, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-45 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ACYL HALIDES |
||
| Acyl halide is one of a large group of organic substances containing the halocarbonyl group, have the general formula R-CO.X (where X is a halogen atom and R may be aliphatic, alicyclic, or aromatic). Acyl is a radical formed from an organic acid by removal of a hydroxyl group. the general formula is RCO, where R may be aliphatic, alicyclic, or aromatic. halide is any compounds of halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine) with another elements and groups. Acyl halides are made by replacing the -OH group in carboxylic acids by a halogen using a halogenating agents. They react readily with water, alcohols, and amines and are widely used in organic synthetic process whereby the acyl group is incorporated into a molecule by substitution called acylation reaction. In substitutive chemical nomenclature their names are formed by adding '-oyl' as a suffix to the name of the parent compound; ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, is an example. | ||
|
|
|