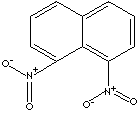
| CAS
NO. |
602-38-0 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
210-016-1 |
| FORMULA |
C10H6(NO2)2 |
| MOL
WT. |
218.17 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2904.20 |
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
Naphthalene, 1,8-Dinitro-
; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Yellow Crystalline Powder |
| MELTING POINT |
171
- 172 C (97 %) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
0.1
g/100ml |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
7.51 |
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: ; Flammability: ; Reactivity: |
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
This compound is sensitive to heat and shock |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
The prefix nitro- indicates the presence of NO2- radical, while nitrate refers
to any salt or ester of nitric acid or the NO3- anion. Nitroso- is the prefix
indicating presence of the group -NO and azo- is for -N=N- group. Some range of
organic compounds containing nitrogen include nitro compounds (RNO2 ), nitroso
compounds (RNO), amines (R3N ), amino acids, and natural alkaloids or
nucleotides. The nitrogen ion in nitro compounds is trigonally planar with 120°
angles. There are two resonance bonds so that the two oxygens are equivalent.
Nitro compounds are strongly basic due to electron withdrawing both inductively
and mesomerically. Historically, they
are abundant in dyes and explosives. Nitro compounds, organic hydrocarbons having one or more NO2
groups bonded via nitrogen to the carbon framework, are versatile intermediate
in organic synthesis.
- Michael
addition
- Reduction
- Henry
Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef
reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion
reaction
- Alkylation,
Acylation, and Halogenation
1,8-Dinitronaphthalene
is an intermediate
for colorants (especially for sulfur colors) and other
organic synthesis.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Yellow Crystalline Powder |
| PURITY
(G.C) |
90.0%
min
|
| 1,5
ISOMER |
6.0%
max
|
|
OTHER
ISOMER
|
4.0%
max
|
|
MELTING
POINT
|
158
- 160 C
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in Bag |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF NAPHTHALENE |
|
Naphthalene is a
white, volatile aromatic hydrocarbon with characteristic odor; insoluble in
water, somewhat soluble in methanol/ethanol, soluble in organic solvents and
very soluble in ether, chloroform, or carbon disulfide. Commercially it is
available in molten form or in flaked form. It has the molecular structure of
two fused or condensed benzene rings sharing two adjacent carbon atoms;
C10H8. Naphthalene is obtained from coal tar which is
distilled in the temperature range of 170 - 230 C and is treated with a sodium
hydroxide solution to remove phenols. Naphthalene is obtained by the isolation
from pyrolysis residue oils, olefin fractions, and petroleum-derived fractions.
The distribution capacity is supposed to be about 60% coal-tar and 40%
petroleum-derived naphthalene in U.S.A. It is an important parent material to
produce numerous substitution products used in the manufacture of dyes,
insecticides, organic solvents and synthetic resins. Phthalic anhydride is
prepared by oxidizing naphthalene to be used in the manufacture of dyes, resins,
plasticizers, and insecticides. Naphthalene sulfonate surfactants and
dispersants, however, have increased their market share significantly and are
expected to drive whatever growth there is for naphthalene. Naphthalene is the
major raw material for Carbaryl, used as a general-purpose insecticide.
Naphthalene is also used for moth repellents, fungicides, lubricants,
explosives, wood preservatives, vermicides and hydronaphthalenes (tetralin,
decalin). Hydronaphthalenes are used for major raw material
for dyes, resins, plasticizers, and insecticides. They are also used in reactive
and process solvents, heat transfer fluid, dye carrier, fuel additives,
lubricants, ore flotation and oilfield chemicals. |
