METHANOL
GENERAL
The major end uses for Methanol are in Formaldehyde), Methyl Tertiary-Buytl Ether (MTBE) (the fastest growing segment of the Methanol market) and in the production of Acetic Acid itself. Methanol is also used in the production of Chloromethanes, Methylamines, Methyl Methacrylate and Dimethyl Terphthalate. Analysts put global methanol demand growth at a moderate 3 to 4 percent annually through 2002, while capacity could increase 5 to 6 percent per year during the period.
PHYSICAL PROPERTY & DESCRIPTION
CAS NO.
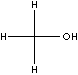
STRUCTURE
Appearance:Colourless Liquid , With Characteristic Odour.
Boiling point: 65C
Melting
point: -98C
Relative density (water = 1): 0.79
Solubility in water:
miscible
Vapour pressure, kPa at 20C: 12.3
Relative vapour density (air =
1): 1.1
Relative density of the
vapour/air-mixture at 20C (air = 1): 1.01
Flash point: 12C c.c.
Auto-ignition temperature: 385C
Explosive limits,
vol% in air: 6-35.6
Octanol/water partition coefficient as log Pow:
-0.82/-0.66
67-56-1
SYNONYM
Methylol
MOL WT.
CH4O
32.042
PRECAUTION IN HANDLING
Physical Dangers:The vapour mixes
well with air, explosive mixtures are easily formed.
Chemical Dangers:Reacts violently with oxidants causing fire and explosion hazard.
Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs):TLV: 200 ppm; 262
mg/m3 as TWA (skin) (ACGIH 1991-1992). TLV (as STEL): 250 ppm;
328 mg/m3 (skin) (ACGIH 1992-1993).
Routes Of
Exposure:The substance can be absorbed into the body by
inhalation and through the skin, and by ingestion.
Inhalation Risk:A harmful
contamination of the air can be reached rather quickly on evaporation of this
substance at 20C.
Effects Of Short-term Exposure:The substance irritates the eyes, the skin and the respiratory tract. The substance
may cause effects on the central nervous system , resulting in loss of
consciousness. Exposure by ingestion may result in blindness and death. The effects may be delayed. Medical
observation is indicated.
Effects Of Long-term Or
Repeated Exposure:Repeated or
prolonged contact with skin may cause dermatitis. The substance may
have effects on the central nervous system , resulting in persistant or
recurring headaches and impaired vision.
APPLICATION
MTBE, formaldehyde, acetic acid, solvents, chloromethanes, methyl methacrylate, methylamines, glycol methyl ethers, dimethyl terephthalate, antifreeze and fuels,
SPECIFICATION
|
Purity |
WT% |
99.85 MIN |
|
PM Test |
- |
50 MIN |
|
Specfic Gravity |
20/20�� |
0.7920~0.7930 |
|
Color |
APHA |
5 MAX |
|
Distil Range |
�� |
64.5~65.5 |
|
Non-Volatile Contest |
��/100�� |
5 MAX |
|
Odor |
- |
PASS |
|
Water |
WT ppm |
1000 MAX |
|
Acidity & Alkanity |
WT ppm |
30 MAX |
|
Acetone |
WT ppm |
30 MAX |
|
Hydro Carbon |
- |
PASS |
|
Cl |
WT ppm |
0.1 MAX |
|
Boiling Point |
�� |
64.5 |
|
Freezing Point |
�� |
97.8 |
|
Flash Point |
�� |
16
(OPEN TYPE) |
|
Explosion Point |
wt % |
36.5 |
|
Ignition Point |
�� |
470 |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ALCOHOL
Alcohols are widely used as solvents, fuels and chemical raw materials. Generally, hydroxyl group compounds are polar, which trends to promote solubility in water. But the carbon chain resist to solubility in water. Short chain alcohols (methanol, ethanol, and propanol) in which the hydroxyl group predominates are miscible in water. Butanol is moderately soluble because of the balance between the two opposing solubility trends. Higher alcohols are practically insoluble in water because of the hydrocarbon chain's trend is stronger. Alcohols are "protic" solvents. Protic refers to a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom, oxygen. Polar protic solvents are compounds that can be represented by the general formula ROH of which water (H2O), methanol (CH3OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are examples. Water-soluble alcohols, low-molecular weight products, are solvents for the manufacture of coatings, dyes and inks, plastics, flavorings, personal-care products, pharmaceuticals, and cleaners. The higher alcohols, slightly soluble in water or insoluble, can provide the proper balance of target properties when solvent-based solvents are formulated for desired viscosity, flowing and leveling, and curing rate and can be used as coupling agents in waterborne coatings.
Alcohols are very weak acids as they lose H+ in the hydroxyl group. Alcohols undergoes dehydration reaction which means the elimination of water molecule replaced by a pi bond between two adjacent carbon atoms to form alkenes under heating in the presence of strong acids like hydrocloric acid or phosphoric acid. Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones respectively. Carboxylic acids are obtained from oxidation of aldehydes. Oxidation in organic chemistry can be considered to be the loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen and reduction to gain hydrogen or loss of oxygen. Tertiary alcohols do not react to give oxidation products as they have no H attached to the alcohol carbon. Alcohols undergoes important reactions called nucleophilic substitution in which an electron donor replaces a leaving group, generally conjugate bases of strong acids, as a covalent substitute of some atom. One of important reaction of alcohol is condensation. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Almost infinite esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. Alcohols are important solvents and chemical raw materials. Alcohols are intermediates for the production of target compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, plasticizers, surfactants, lubricants, ore floatation agents, pesticides, hydraulic fluids, and detergents.
Carbinol is a primary alcohol with general formula RCH2OH. In carbinol nomenclature system, the term of carbinol is methanol itself and other groups are considered to have replaced one of the methanol hydrogen atoms to describe larger alcohols as derivatives of carbinol. This nomenclature system is particularly useful when the groups attached to the methanol carbon are large, aromatic, and cyclo groups. Benzyl alcohol is called phenylcarbinol or benzenecarbinol while benzyl carbinol is phenylethyl alcohol.