DIETHYL ETHER
GENERAL
PHYSICAL PROPERTY & DESCRIPTION
CAS NO.
STRUCTURE
Appearance:
clear gas, colorless,Slightly ethereal
pH: Not available.
Vapor Pressure: 72 psig @ 77F Vapor Density: 3.18
(tetrafluoroethane) Evaporation Rate: >1.0 (Butyl
Acetate=1) Viscosity: Not available.
Boiling Point:
34 - 35 deg C
Freezing/Melting Point: Not available.
Solubility: 5.2% at 77¦F/1atm
Specific
Gravity/Density: 1.2
60-29-7
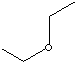
SYNONYM
ethyl Eether
MOL WT.
C4H10O
74.12
PRECAUTION IN HANDLING
Flammable
liquid and vapors. Keep container closed. Do not breathe
vapors. Avoid contact with skin, eyes and mucous membranes.
Keep away from heat, sparks and flame. Electrically
ground all handling equipment. Protective neoprene or
rubber gloves and apron are recommended. Ensure contents
are at or below room temperature before opening container(s).
Store
in an area designed for storage of flammable liquids.
Protect
from temperature extremes and sunlight, and store away
from incompatible substances and in accordance with
29 CFR 1910.106. Avoid acids, bases, oxidizers, explosives,
nitrogen-fluorine compounds, sulfites, perchlorates.
Flammable
liquid and vapor. Once liquid solvent has been completely
dispensed, containers which appear "empty"
should be handled in the same manner as when they were
"full" of liquid solvent.
APPLICATION
SPECIFICATION
|
Purity |
WT% |
Min 98.0 |
|
Carbon Dioxide |
ppm |
- |
|
Free MEOH |
ppm |
- |
|
Methyl Formate |
ppm |
- |
|
Evaporation Residue |
ppm |
- |
|
Specific Gravity(20��) |
- |
Max 0.723 |
|
Moisture |
ppm |
- |
|
Appearance |
- |
- |
|
Non Volatile Residue |
ppm |
Max 20 |
|
Acidity |
ppm |
Max 20 |
|
Peroxide |
- |
- |
|
Aldehyde |
mg/100ml |
Max 1.0 |
|
Acetylene |
ppm |
Max 10 |
|
Color |
APHA |
Max 20 |
|
Boiling Point |
�� |
34.5 |
|
Freezing Point |
�� |
-116.3 |
|
Flash Point |
�� |
-45 |
|
Auto Ignition Point |
�� |
180 |
|
Vapor Pressure |
��Hg(20��) |
440 |
|
Vapor Density (Air=1) |
- |
2.55 |
|
Solubility In H2O |
WT%(20��) |
6.9 |
|
LEL |
VOL % |
1.9 |
|
UEL |
VOL % |
48.0 |
|
Evaproation Rate(BUAL=1) |
- |
37.5 |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ETHER