| CAS
NO. |
7481-89-2 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
|
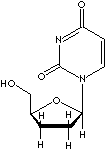
| FORMULA |
C9H13N3O3 |
| MOL
WT. |
211.22 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
2',3'-Dideoxycytidine; ddC; Hivid;
Dideoxycytidine;
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to
off-white crystalline powder |
| MELTING POINT |
215 - 218 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
|
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Zidovudine is a thymidine analogue in which the 3'-hydroxy (-OH) group is
replaced by an azido (-N3) group. It is used in the management of human
immunodeficiency virus. It is an antiretroviral agent that inhibits replication
of some retroviruses. It is converted into the active metabolite zidovudine
5'-triphosphate which inhibits the activity of the HIV (human immunodeficiency
virus) reverse transcriptase within cells. The viral DNA growth is terminated
due to the lack of 3'-OH group which prevents the formation of the essential for
DNA chain elongation (5' to 3' phosphodiester). Zalcitabine
(2',3'-dideoxycytidine), an analogue of 2'-deoxycytidine which does not have -OH
group both at 2' and at 3' position, is an antiretroviral agent used in
combination with zidovudine. Zalcitabine is converted into the active metabolite
dideoxycytidine 5'-triphosphate that inhibits the action of reverse
transcriptase. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine
and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine are used in the study for antiviral and anticancer
researches. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white to
off-white crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY |
99.0%
min
|
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+74°
~ +76° (C=0.6 in water)
|
|
WATER
|
0.5%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
10ppm
max
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING |
0.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 40, Safety Phrases: 22-36 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF DIDEOXYNUCLEOSIDE |
|
Dideoxynucleoside
is a synthetic nucleoside analogue which
lacks two hydroxyl groups on 2' and 3'
carbon. This modification prevents the formation of
phosphodiester linkages which are needed for the completion of nucleic acid
chains. Some 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides acts as a
chain-terminator of viral DNA by inhibiting the enzyme reverse
transcriptase. These compounds inhibit HIV replication and thus have antiretroviral activity
in the treatment of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
|
