PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
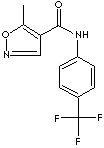
Leflunomide derived from isoxazole is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor by interfering with the synthesis of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase(DHODH), resulting in inhibiting T and B cell proliferation or growth. It is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. It reduces the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and slows progressive deformities of the joints. The chemical designation is N-(4´-trifluoromethylphenyl)-5- methylisoxazole-4- carboxamide. It is a white crystals powder; melting point 165 - 166 C; administered orally.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies
ASSAY (HPLC)
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
10ppm max
The main categories of drugs to treat or slow down rheumatoid arthritis are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), gold compounds (sodium aurothiomalate, auranofin), analgesics, corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs which are originally used to prevent the rejection of transplanted organs and tissues. Immunosuppressive drugs are also used to treat myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis. Most of immunosuppressive drugs have their own potentially serious side effects. They should be used in small doses. They acts by suppressing cell growth or multiplication of both T cells and B cells and interfering with the synthesis of nucleic acids. There are newer biologic therapies such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and interleukin-1 receptor antagonists.
Some examples of immunosuppressive drugs to slow down rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Azathioprine
- Cyclophosphamide
- Cyclosporine
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Leflunomide
- Methotrexate
- Penicillamine