| ERYTHROMYCIN STEARATE | |||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||
| CAS NO. | 114-07-8 (Base), 643-22-1 (Stearate) | ||||
| EINECS NO. | 211-396-1 | ||||
| FORMULA | C37H67NO13-C18H36O2 | ||||
| MOL WT. | 1018.59 | ||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2941.50.0000 | ||||
|
TOXICITY |
Women TDLo (Oral): 60mg/kg (60mg/kg). Gastrointestinal: changes in structure or function of endocrine pancreas. Gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting | ||||
| SYNONYMS | Bristamycin; Qidmycin; Pfizer-e; Pantomicina; Wyamycin; Gallimycin; | ||||
|
Dowmycin E; Eratrex; Erypar; Ethril; Meberyt; Pantomicina; Erythromycin stearic acid salt; Abboticine; (2R,3S,4S,5R,6R,8R,10R,11R,12R,13R)-5- (3,4,6- Trideoxy -3-dimethylamino- beta-D-xylo- hexopyranosyloxy) -3- (2,6-dideoxy-3-C- methyl-3- O-methyl- alpha-L-Ribo- hexopyranosyl oxy)- 13-ethyl-6,11,12- trihydroxy -2,4,6,8,10,12- hexamethyl-9-oxo tridecan- 13-olide monostearate; |
|||||
|
SMILES |
O1[C@H](C[C@@]([C@H]([C@@H]1C)O)(C)OC)O[C@H]1[C@H](C)[ C@@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@H]2O)N(C)C)C)[C@ @](C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@](O)(C)[C@H] (OC(=O)[C@@H]1C)CC)(O)C.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O | ||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antibacterial, Antibiotic, Anti-infective Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent, Macrolide |
||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | fine white to off white powder | ||||
| MELTING POINT | 100- 104 C | ||||
| BOILING POINT |
|
||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | <1 mg/mL at 22 C | ||||
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | >=100 mg/mL at 22 C (in ethanol) | ||||
| pH | |||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| ||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | ||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| ||||
| FLASH POINT |
| ||||
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS |
|||||
|
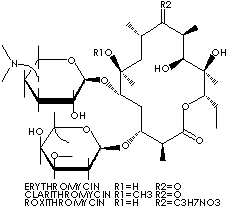
The macrolides, derived from Streptomyces bacteria, are a group of antibiotics that inhibits protein synthesis by bacteria at the 50S ribosome. They are characterized by a macrocyclic ring (a large ring molecule with many functional groups bonded to it) and a large lactone ring in the molecular structure. They are usually used for respiratory tract, skin, and genitourinary infections. Erythromycins inhibits protein synthesis in some microorganisms and are used as an antibiotic against many kinds of infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, including some beta-hemolytic streptococci, pneumococci and staphylococci as well as gram-negative bacteria and some fungi. It is used also in the treatment of upper and lower respiratory tract infections caused by chlamydia trachomatis and intestinal amebiasis. It's application include the treatment of syphillis in patients who may be allergic to penicillin and the treating Legionnaire's disease. Examples of macrolides are:
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erythromycin http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/
https://www.imsa.edu/ |
|||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Fluffy colorless powder | ||||
| IDENTIFICATION |
Complies |
||||
| ASSAY | 86.0% min (Erythromycin Stearate) | ||||
|
|
620 mcg/mg min (on the anhydrous Erythromycin basis) |
||||
| FREE STEARIC ACID |
14.0% max |
||||
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
1.0% max |
||||
|
WATER |
4.0% max |
||||
| pH |
7.0 - 10.0 |
||||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||||
| PACKING | | ||||
| HAZARD CLASS | |||||
| UN NO. | |||||
|
MACROLIDES |
|||||
|
|
|||||