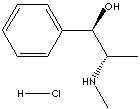
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
50-98-6
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
passes test A,B
98.5.% - 101.5%
RELATED SUBSTANCE
Complies
OPTICAL ROTATION
-33° ~ -35° (C=4 in water)
VOLATILES
Complies
SOLVENT RESIDUE
Complies
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
0.5%
max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF TYRAMINE & TRYPTAMINE
Tyramine [4-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol] is a monoamine compound of 4-hydroxy phenethylamine. It is derived from tyrosine, an amino acid (protein building block) that is the precursor of norepinephrine. It, through its effect on neurotransmitters, may affect several health conditions, including Parkinson's disease, depression, alcohol withdrawal support, and Phenylketonuria. (PKU). Tyramine is naturally found in plant and animal tissues, certain cheeses and ergot or produced synthetically. It is metabolized by monoamine oxidase. Tyramine or its derivatives can be used in pharmaceutical industry such as:
- Sympathomimetic or adrenergic drugs themselves or intermediate of them.
- Intermediate for bezafibrate used in the treatment of high cholesterol levels.
- Determination of peroxide activity in the fluorescence enzyme immunoassay for insulin.
- False transmitter.
Tryptamine [3-(2-Aminoethyl)indole] is a biologically important monoamine compound derived by the decarboxylation of tryptophan, indole side chain amino acid. In addition to its function to build the structure of protein, tryptophan is a precursor for neurotransmitter and neurohormone. Tryptamine (biological monoamine) effects vasoconstriction by causing the release of norepinephrine at postganglionic nerve endings. Several mental disorders and health conditions are explained as due to either an excess or deficiency of monoamines. There are many natural tryptamines in both animal and plant as well as synthetics modified by chemical constituents and substituted at appropriate positions in the motif. Common tryptamine class compounds include;
- Bufotenine (CAS #: 487-93-4): (5-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, pressor agent, epinephrine-like.
- DMT (CAS #: 61-50-7): N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, a psychedelic and hallucinogenic.
- Melatonin (CAS #: 73-31-4, 8041-44-9): N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, biological clock hormone.
- Psilocin: 4-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
- Psilocybin (CAS #: 520-52-5): 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, a hallucinogenic.
- Serotonin (CAS #: 50-67-9): 5-Hydroxytryptamine, a vasoconstrictor.
- Sumatriptan( CAS #: 103628-46-2) 4-Hethylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, selective serotonin antagonist used in the treatment of migraine headache.
PRICE INFORMATION