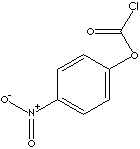
4-NITROPHENYL CHLOROFORMATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
- 4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (CAS NO. 7693-46-1): a reagent for the synthesis of mixed, activated carbonates and thiocarbonates, activated urethanes, and other compounds. Used to synthesize a cleavable, heterobifunctional cross-linker for reversible conjugation of amines to thiol-modified DNA. Employed in the preparation of poly(oxyethylene) modified dextrans.
- Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonylchloride (CAS No. 28920-43-6): a reagent for derivatizing amino acids and for introducing N-Fmoc amino acids for solid-phase peptide synthesis and for the synthesis of a bicyclic proline analog. FMOC protection is important in solid phase peptide synthesis because its removal with piperidine solution does not disturb the acid labile linker between the peptide and the resin. Very stable in acidic condition, and moderately stable in inorganic base.
- Benzyl chloroformate (CAS No. 501-53-1): a reagent useful for the introduction of the carboxybenzyl (Cbz or Z) protecting group for amines. Easily deprotected under hydrogenation or triethyl silane.
- Ethyl chloroformate (CAS No. 541-41-3): a reagent for the introduction of the ethyl carbamate protecting group and for the formation of carboxylic anhydrides. Used to convert carboxylic acids to nitriles.
- Chloroethyl Chloroformate (2-Chloroethyl chloroformate: CAS No. 627-11-2, 1-Chloroethyl chloroformate:CAS No. 50893-53-3): a reagent for the selective N-dealkylation of tertiary amines. and for the synthesis of alkyl 1-chloroethyl carbonates. Useful in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals (e.g.: Cefpodoxime, Candesartan, Ampiroxicam, Bacampicillin)
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
MELTING POINT
78 C min