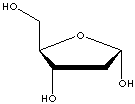
| Ribose is a pentose (five-carbon sugar) that is a component of the ribonucleic
acid (RNA), where it alternates with phosphate groups to form the 'back-bone' of
the RNA polymer and binds to nitrogenous bases. Ribose phosphates are components
of the nucleotide coenzymes and are utilized by microorganisms in the synthesis
of the amino acid histidine. Its close relative, deoxyribose, is a constituent
of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), where it alternates with phosphate groups to
form the 'back-bone' of the DNA polymer and binds to nitrogenous bases. The
presence of deoxyribose instead of ribose is one difference between DNA and RNA.
Ribose has one more oxygen atom in its molecule than deoxyribose. Ribose has a
five member ring composed of four carbon atoms and one oxygen. Hydroxyl groups
are attached to three of the carbons. The other carbon and a hydroxyl group are
attached to one of the carbon atoms adjacent to the oxygen. In deoxyribose, the
carbon furthest from the attached carbon is stripped of the oxygen atom in what
would be a hydroxyl group in ribose. The sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) molecules
in the nucleic acid are all oriented in the same direction. Their carbon atoms
are numbered: the 5' carbon atom is always on the side of the sugar molecule
that faces the leading end, while the 3' carbon atom always faces the tail end.
Nucleotide is the structural unit of a nucleic acid. A nucleotide consists of
either a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine) , a pentose sugar
(ribose or deoxyribose) and a phosphate group attached at the 5' position on the
sugar. A nucleoside consists of only a pentose sugar linked to a purine or
pyrimidine base, without a phosphate group. Purine bases are Adenine, Guanine
and Hypoxanthine (examples of purine nucleosides are
Adenosine, 2'-Deoxyadenosine, Guanosine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine,
Inosine, 2'-Deoxyinosine). Pyrimidine bases are Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
(examples of pyrimidine nucleosides are Cytidine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine,
5-Methyluridine, 2'-Deoxy-5-Methyluridine, Uridine,
2'-Deoxyuridine). The nucleoside derivatives involved in important functions in cellular
metabolism and are used to synthesize enzyme inhibitors, antiviral agents, and
anticancer agents. |