PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
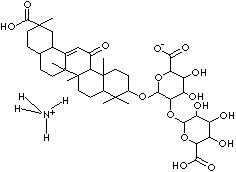
C1([C@H]2[C@@]([C@@]3(C([C@H]4[C@@](CC[C@@](C4)(C(O)=O) C)(C) CC3)=C1)C)(CC[C@@H]1[C@@]2(CC [C@@H](C1(C)C)O [C@@H]1[C@H]( O[C@@H] 2O[C@@H] ([C@@H](O)[C@@H]([C@H]2O)O)C(O)=O)[C@H] ([C@H]( O)[C@H](O1)C(O)=O)O)C)C)=O.N
CLASSIFICATION
Anti-Inflammatory agent, Triterpenoid
EXTRA NOTES
A widely used anti-inflammatory agent isolated from the licorice root. It is metabolized to glycyrrhetinic acid, which inhibits 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and other enzymes involved in the metabolism of corticosteroids. Therefore, glycyrrhizic acid, which is the main and sweet component of licorice, has been investigated for its ability to cause hypermineralocorticoidism with sodium retention and potassium loss, edema, increased blood pressure, as well as depression of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. (MeSH)
Other RN: 1407-03-0, 42618-06-4, 52248-53-0, 97635-37-5, 202522-36-9
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
Soluble in glacial acetic acid
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Three varieties of the species have been reported; Spanish licorice and Italian licorice are assigned to G. glabra var. typica, Russian licorice is G. glabra var. glandulifera, and Persian and Turkish licorices are G. glabra var. violacea. About 90 kinds of phenolic compounds have been isolated from the plants. About 50 of them are substituted with isoprenoid group(s), e.g., 3-methyl-2-butenyl (prenyl) group, 2,2-dimethylpyran ring, etc. These G. glabra could be classified into two groups with the constituents of isoprenoid-substituted flavonoids. Type I licorice is Spanish and Russian licorices. The main isoprenoid-substituted flavonoid of the plants is a pyranoisoflavan, glabridin. The 5-position of most flavonoids from the type I plants is unsubstituted, glabrene, glabrol, 3-hydroxyglabrol. Type II licorice is Chinese and Kyrghiz G. glabra. From these plants, both 5-unsubstituted flavonoids and 5-oxygenated flavonoids (e.g., 3',8-diprenylated dalbergioidin, have been isolated. Nevertheless, most flavonoids from these plants are 5-hydroxy- or 5-methoxy-flavonoids. (http://www.iupac.org/)
Glycyrrhizin, one of the main components found in licorice, is believed to contribute to the herb's healing properties. Laboratory studies have reported that glycyrrhizin reduces inflammation, promotes secretion of mucous (usually through coughing), soothes irritation, protects the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, and stimulates the activity of the adrenal glands (regulates cortisol, the stress hormone). ( http://www.umm.edu/)
Glycyrrhiza (the dried rhizome and roots of various species of Glycyrrhiza) contains triterpene glycoside called Glycyrrhizin, Glycyrrhizic acid, or Glycyrrhizinic acid (salts are called Glycyrrhizin) which is converted to glycyrrhetinic acid (the aglycone) and two moles of gucuronic acid (the glycone) on hydrolysis. Glycyrrhizinic acid is potentially 50 times sweeter than sucrose. Licorice (liquorice in British spelling) is the alteration of Glycyrrhiza glabra, a Mediterranean perennial plant with blue pealike blossoms. Glycyrrhiza is the active principle for sweetening, flavoring and pharmaceutical applications. It is effective in treatment of peptic ulcer. It is used in brewing and for confectionery and tobacco flavorings. It is frequently used in medicines to mask the unpleasant flavours. It has been used medicinally for highly effective coughs and as a mild laxative. It promotes the ejection of mucus or exudate from the lungs, bronchi, and trachea; sometimes extended to antitussives. Glycyrrhetinic acid has corticosteroid-like structure, thus is useful as an anti-inflammatory and co-emulsifier to treat skin disorders and in cosmetics.
Pharmacological actions:
- Anti-Inflammatory
- Antiallergic
- Antibacterial
- Antiviral
Glabridin (the main isoflavan compound in fraction of licorice extract), and glabrene ( the main isoflavene) demonstrats significant antioxidant and estrogen-like activities. Some data suggest that they protect low-density lipoprotein against lipid peroxidation.
|
|
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
7.0% max
+44.0° ~ +52.0° (c = 1 in ethanol(1):water(1))
ARSENIC
3ppm max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
CHLORIDE
0.015% max