|
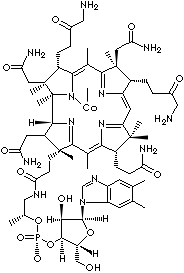
Cobalamin [cobal(t) + (vit)amin] is a compound containing the substituted corrin
ring (polyaromatic ring consisting of 4 pyrrole subunits which are joined by
methylene links on opposite sides and the two of the pyrroles are joined
directly) and 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole, as the aglycon attached by a glycosyl link. Vitamin B12 is a cyanide ion
substituted cobalamin derivative (cyanocobalamin) with the presence of cobalt
mineral at 6 position. Vitamin B12 is the only vitamin which contains metal ion
(trivalent cobalt). Cobalamin is sometimes defined as the synonym of Vitamin
B12, although they are not same compound but closely related compounds to
fulfill folic acid role. Vitamin B12 is typically any substituted cobalamin
derivative having similar biological activity. Hydroxocobalamin (abbreviated
OHCbl), a cobalamin
derivative in which the substituent is a hydroxyl group, is called vitamin B12b.
Methylcobalamin (abbreviated MeCbl) is a cobalamin derivative in which the substituent is a methyl
group. MeCbl is involved in several biosynthesis including methionine.
Adenosylcobalamin (abbreviated AdoCbl)is a cobalamin derivative in which the substituent is
deoxyadenosyl. MeCbl and AdoCbl are two metabolically active coenzyme forms synthesized upon ingestion of vitamin
B12 and are the predominant form in the liver and in the serum respectively.
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble hematopoietic vitamin. It is needed in various
body processes including the manufacture and the maintenance of red blood cells,
the synthesis of DNA, the stimulate of nerve cells, the growth promotion and
energy release. Vitamin B12 is the antipernicious anemia factor and essential
for normal hemopoiesis. It is used to treat the absence of intrinsic factor
which is responsible for the absorption of B12 from the intestine; including
particularly pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias and associated
neuropathy. Vitamin B12 is administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or
orally. |
|
Vitamin
B is a group of water-soluble vitamins that include thiamine (vitamin B1), riboflavin
(vitamin B2), riboflavin 5'- phosphate, nicotinic acid, Vitamin B6 Group
(Pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine), panthothenic acid (vitamin B3 or
vitamin B5), inositol,
p-aminobenzoic acid, biotin (vitamin B7), folic acid (vitamin B9), and vitamin B12 (cobalamins)
|