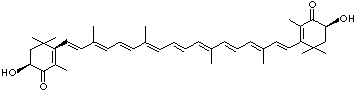
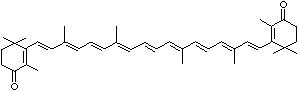
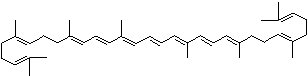
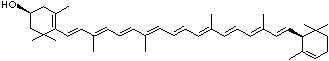
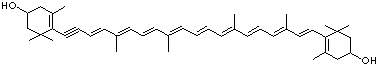
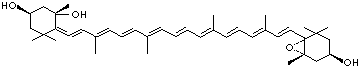
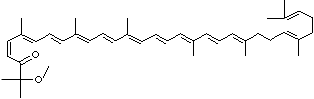
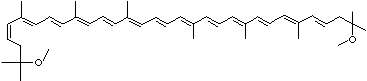
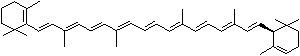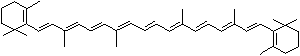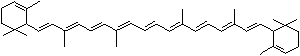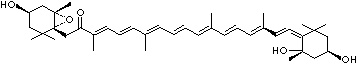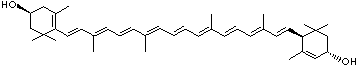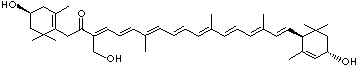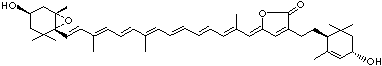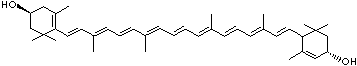LUTEIN
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
![]()
H.S. CODE
3212.90.0000
TOXICITY
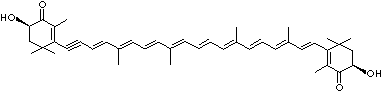
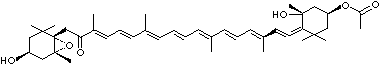
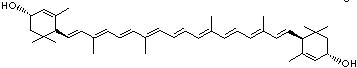
4',5'-Didehydro-5',6'-dihydro-beta,beta carotene-3,3'-diol; Xanthophyll; Bo-Xan; Lutein; all-trans-Lutein; gamma-Lutein; Other RN: 1407-74-5; 148124-35-0; 25312-96-3; 28368-07-2; 34026-62-5; 34445-91-5
SMILES
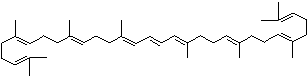
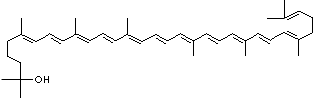
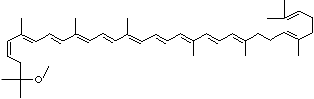
C1([C@H](C(=C[C@@H](C1)O)C)\C=C\C(=C\C=C\C(=C\C=C\C= C(\C=C\C=C(\C=C\C=1C(C[C@H](O)CC1C)(C)C)C)C)C)C)(C)C
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
orange to red crystalline powder
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
- Carotenes
- alpha-Carotene
- beta-Carotene
- gamma-Carotene
- delta-Carotene
- Lycopene
- Neurosporene
- Phytofluene
- Phytoene
- Xanthophylls
- Astaxanthin
- Cantaxanthin
- Cryptoxanthin
- gamma-Lutein (xanthophyll)
- Zeaxanthin
Carotene: though carotene is the simplest of a group of natural pigments called carotenoids, it has an unsaturated and long aliphatic hydrocarbon chain. It is found as a fat-soluble pigment in many higher plants of dark green leafy and yellow vegetables such as carrots, collards, turnips, sweet potatoes, and squash, and in yellow fruits such as apricots, oranges, peaches, and cantaloupes. Carotene is thought to transport light energy for photosynthesis or contribute to reduction reaction. It is important in animal biology as it is are converted to retinol in the body by an enzyme in the intestinal wall and the liver. Carotene occurs in several isomeric forms: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, and zeta of which the form of beta acts as an antioxidant nutrient protecting the body from damaging molecules called free radicals and an immune system booster as it is converted to vitamin A (retinol), important in animal biology as the main dietary source. One molecule of beta-carotene splits into two molecules of vitamin A and thus Beta-carotene is called provitamin A. Cryptoxanthin is a yellow carotenoid widely distributed in egg yolk, green grass, yellow corn which can be converted into vitamin A in the body. Cryptoxanthin is the major precursor of vitamin A together with beta-carotene in humans.
Wikipedia Linking:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lutein
http://chiro.org
....Lutein and Zeaxanthin belong to the zanthophyll family of carotenoids and are
the two major components of the macular pigment of the retina. The macula lutea,
or "yellow spot" in the retina is responsible for central vision and visual
acuity. Lutein and Zeaxanthin are the only carotenoids found in both the macula
and lens of the human eye, and have dual functions in both tissues- to act as
powerful antioxidants and to filter high-energy blue light. In addition to
playing pivotal roles in ocular health, Lutein and Zeaxanthin are important
nutrients in the prevention of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and lung
cancer....
APPEARANCE
orange to red crystalline powder
PURITY
20.0% min
3ppm max
1.0% max
ANALYSIS
Yeast and mold: not more than 100/g
E.coli: neagative
Salmonella: neagative
SOLVENT RESIDUAL
50ppm max
|
Astacin |
|
|
Astaxanthin |
|
| Bixin [CAS#: 6983-79-5 (cis-) 39937-23-0 (trans-)] |
|
| Canthaxanthin [CAS#: 514-78-3] |
|
| Capsanthin [CAS#: 465-42-9] |
|
|
alpha-Carotene |
|
|
beta-Carotene |
|
|
gamma-Carotene |
|
|
delta-Carotene |
|
|
epsilon-Carotene |
|
|
zeta-Carotene |
|
|
alpha-Cryptoxanthin |
|
|
Diatoxanthin |
|
|
Didehydroastaxanthin |
|
|
Fucoxanthin |
|
|
Fucoxanthinol |
|
|
Lactucaxanthin |
|
|
gamma-Lutein |
|
| Lycopene [CAS #: 502-65-8] |
|
|
Neoxanthin |
|
|
Neurosporene |
|
| Norbixin [CAS #: 626-76-6 (cis-) 542-40-5 (trans-)] |
|
|
Peridinin |
|
|
Phytoene |
|
|
Rhodopin |
|
|
Siphonaxanthin |
|
|
Spheroidene |
|
|
Spheroidenone |
|
|
Spirilloxanthin |
|
|
Uriolide |
|
|
Violaxanthin |
|
|
Zeaxanthin |
|