PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
128-37-0
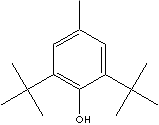
C6H2(OH)(CH3)(C(CH3)3)2
220.34
H.S. CODE
UN NO.
TOXICITY
c1(c(O)c(C(C)(C)C)cc(c1)C)C(C)(C)C
CLASSIFICATION
Antioxidant
EXTRA NOTES
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 3.
FEMA No. 2184
EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 022105
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
265 C
1.048
7.6
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
127 C
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.datasync.com/
BHT molecules host seven CH3 methyl groups. A methyl group
consists of three hydrogen atoms bonded to a carbon atom which is linked to the
remainder of a molecule.(2) In the colored stick diagram, the methyl group
hydrogen atoms are shown as match heads to remind readers of their
roles as hydrogen donor free radical scavengers. Their anthromorphic motto might
be "Light my fire!" (These last two sentences are written by a
non-chemist. It may turn out that something else about the molecule
causes it's radical scavenging activity. Input is welcome!)
Local: Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), chemically 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol (DBPC), is a white crystalline solid with a faint characteristic odor. It is insoluble in water and in propylene glycol, but is freely soluble in alcohol. It is obtained by alkylation of p-cresol with isobutene or by monobutylation of m,p-cresol mixtures. BHT is used as a chemical antioxidant for food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals much like butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA). BHA is insoluble in water, but is freely soluble in alcohol and in propylene glycol. BHA is the mixture of 3-tert-buryl-4-hydroxyanisole (typically 90% w/w) and 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. These phenol derivatives react with the free radicals (called free radical scavengers) can slow the rate of autoxidation that can lead to changes in the food's color and taste. Other antioxidants for food are phosphoric acid, citric acid, gallic acid, ascorbic acid and their esters which form complexes with the pro-oxidative metal traces. Antimicrobial process is also important in preserving foods. BHT and BHA are used as an antioxidant in plastics, elastomers and petroleum (lubes, greases and waxes), practically bigger market size than food field. BHT is also used as a stabilizer to inhibit the auto-polymerization of organic peroxides.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ANTIOXIDANT: Antioxidant is a substance added in small quantities to hydrocarbons which are susceptible to oxidation, such as rubbers, plastics, foods, and oils to inhibit or slow oxidative processes, while being itself oxidized. Antioxidants work in two different ways. In primary antioxidants (also called free-radical scavengers), antioxidative activity is implemented by the donation of an electron or hydrogen atom to a radical derivative. These antioxidants are usually hindered amines (p-Phenylene diamine, trimethyl dihydroquinolines, alkylated diphenyl amines) or substituted phenolic compounds with one or more bulky functional groups such as a tertiary butyl at 2,6 position commonly. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a common example of hindered phenolic antioxidant. The reaction rate, or carbocation stability, in SN1 mechanism is 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3 (no SN1) so, tertiary alkyl moiety exists in lots of phenolic antioxidant compounds. Primary antioxidants are free radical scavengers which combine with peroxy radicals and break autocatalytic cycle. In secondary antioxidants ( also called peroxide decomposers), activity is implemented by the removal of an oxidative catalyst and the consequent prevention of the initiation of oxidation. Examples of peroxide decomposer type of antioxidant are trivalent phosphorous and divalent sulfurcontaining compound such as sulfides, thiodipropionates and organophosphites. Synergistic effect is expected when primary antioxidants are used together with secondary antioxidants as primary antioxidants are not very effective against the degradation by UV oxidation. Sometimes, chelating agents are added to scavenge metal impurities which can initiate decomposition.
FOOD GRADE
APPEARANCE
MELTING POINT
69 - 70 C
MOISTURE
0.1% max
SULFATE
0.002% max
0.0004% max
As
0.0001% max
0.02% max
INDUSTRIAL GRADE
APPEARANCE
MELTING POINT
68.5 - 70 C
FREE METHYL PHENOL
0.3% max
ASH
0.03% max
MOISTURE
0.1% max
PRICE INFORMATION