| CAS
NO |
600-14-6 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
209-984-8 |
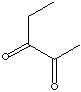
| FORMULA |
CH3COCOC2H5 |
| MOL
WT. |
100.12 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2914.19 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oralrat
LD50: 3000 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Pentane-2,3-dione;
Acetyl propionyl; |
| Acetyl
propanal; Beta,gamma-dioxopentane; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
to yellow liquid |
| MELTING
POINT |
-52
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
110
- 112 C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.957 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
partially
soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
3.45 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
1.404
± 0.002 |
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1; Flammability: 4; Instability: 0 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
18
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
Diketones
are used as a solvent for cellulose acetate, paints,
inks, lacquers and as starting
materials for the manufacture of target molecules including dyes, pesticides and drugs.
2,3-Pentanedione is used as a constituents of synthetic flavouring agents
(Odor description : buttery,
cheesy, sweet, nutty, fruity, creamy, caramel). Some
examples of aliphatic alpha-diketones found in food
additives are:
- 2-Acetoxy-3-butanone [CAS
RN: 4906-24-5]
- Butan-3-one-2-yl-butanoate [CAS
RN: 84642-61-5]
- Diacetyl [CAS
RN: 431-03-8]
- 2,3-Pentanedione [CAS
RN: 600-14-6]
- 4-Methyl-2,3-pentadione [CAS
RN: 7493-58-5]
- 2,3-Hexadione [CAS
RN: 3848-24-6]
- 3,4-Hexadione [CAS
RN: 4437-51-8]
- 5-Methyl-2,3-hexadione
[CAS RN: 13706-86-0]
- 2,3-Heptanedione [CAS
RN: 96-04-8]
- 2,3-Undecadione [CAS
RN: 7493-59-6]
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
to yellow liquid |
|
PURITY
(G.C.)
|
98.0%
min
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.952
- 0.962
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
3
(Packing Group: II) |
| UN
NO. |
1993 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
Hazard
Symbols: F, Risk Phrases: 11, Safety
Phrases: 9-16-33
FEMA
Number: 2841 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF DIKETONE |
Diketone is a molecule
which contains two ketone carbonyl groups. Diacetyl (CH3COCOCH3),
2,3-butadione, is the simplest aliphatic diketone.
It is an alpha-diketone which has two ketone groups side-by-side.
Usually, alpha-diketone imparts a carmel like or buttery flavor.
Diketone compounds take a role in creating various
fragrances. Bezil (C6H5COCOC6H5)
is
an aromatic diketone, the fundamental structure of
photo sensitive molecule which is broken down into free radicals upon exposure to ultraviolet
radiation. Acetoacetone
is a beta-diketone which two ketones are separated only by one carbon.
The beta-ketone is stable as a conjugated enol rather than a diketone
due to the delocalization which makes the counterion more stable and less likely to regain the
proton. Ascorbic acid is an example of enol compound. Enol compounds form complexes with many transition metal
ions. These compounds are readily soluble in organic solvents. They are widely used as chelating
agents, ligands, and catalyst precursors.
Acetoacetic acid and its esters contain active
methylene groups which have relatively acidic alpha-protons due to H atom
adjacent to two carbonyl groups. The reactivity of its methylene group provide
the sequence of reactions of alkylation, hydrolysis of the esters and
decarboxylation resulting in substituted ketones. Acetoacetic acid derivatives
are important aliphatic parts adjoining azo dyes and pigments.
Aacetoacetate
is one of Ketone bodies which are the
end-products of rapid or excessive fatty acid breakdown in the human body. Para-benzoquinone
and its derivatives belong to 1,4-diketone family. Benzoquinone is used as an oxidizing agent
in organic chemistry and is a common constituent of biologically molecules like
Vitamin K1. Quinones serves as electron acceptors in electron transport chains such as in
photosynthesis, and aerobic
respiration. Diketene
derivatives find versatile applications in making biomolecules, agrochemicals, dyes, pigments,
pharmaceuticals including vitamins, and stabilizers for PVC and
polyester. They are used as components for fragrances and as solvents. Diketones
undergo the reversible and irreversible addition reactions include;
- Aldol Reactions
- Alkylation of Enolate Anions
- Clemmensen Reduction
- Cyanohydrin Formation
- Enamine Formation
- Hemiacetal and
Acetal Formation
- Hydration Formation
- Imine Formation
- Wolff-Kishner Reduction
|
