PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
14375-45-2 [((±)-Abscisic acid]
21293-29-8 [(+)-Abscisic acid]
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
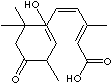
[C@@]1(C(CC(=O)C=C1C)(C)C)(/C=C/C(=C\C(=O)O)C)O
CLASSIFICATION
Plant growth regulator
EXTRA NOTES
Abscisic acid (ABA) is an isoprenoid plant hormone (phytohormone) synthesized in all parts of plants and involved in many plant developmental processes. ABA is involved in establishing dormancy and regulation of stress responses. ABA inhibits fruit ripening, seed germination, photosynthesis and kinetin biosynthesis.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Health hazard: 0, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 0
Stable under ordinary conditions. Light/air sensitive.
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Abscisic acid
Google Scholar Search - Abscisic acid
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Abscisic acid
PubChem Compound Summary - Abscisic acid
Drug Bank - Abscisic acid
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Abscisic acid
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Abscisic acid
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Abscisic acid
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - Abscisic acid
http://www.plant-hormones.info/
Nature of Abscisic Acid: Abscisic acid is a single compound unlike the auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins. It was called "abscisin II" originally because it was thought to play a major role in abscission of fruits. At about the same time another group was calling it "dormin" because they thought it had a major role in bud dormancy. The name abscisic acid (ABA) was coined by a compromise between the two groups. Though ABA generally is thought to play mostly inhibitory roles, it has many promoting functions as well(Arteca, 1996; Mauseth, 1991; Raven, 1992; Salisbury and Ross, 1992).
http://www.ars.usda.gov/
Abscisic Acid-The Plant Stress Hormone
Local:
Abscisic acid is one of five (or more) major plant hormones (Auxin, Cytokinins, Gibberellins, Ethylene and Abscisic acid). It can be classified as a shock hormone which are produced in response to rapid developing stress situations. Abscisic acid is ubiquitous in higher plants. The the highest levels are found in young leaves and developing fruits and seeds at the beginning of the winter season. Auxin and cytokinin are growth hormones. Gibberellins and ethylene are
known as stress hormones. Though each plant hormone evokes many different specific biochemical, physiological, or morphological responses, the effects of different hormones overlap and may be stimulatory or inhibitory to regulate plant development and growth. Abscisic tends to disrupt various aspects of plant growth to develop fruits and augment sugar content. Accordingly, it can be classified as the growth retardants, which can be sub-classified as gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitors or compounds which are not involved in inhibiting gibberellin biosynthesis. [abscisic acid, cimetacarb, daminozide, dikegulac, maleic hydrazide, mefluidide, and morphologically active substances (morphactins: chlorfluren, chlorflurenol, dichlorflurenol, flurenol)].
Some commercial growth retardants are;
- Abscisic acid [(2Z,4E)-5-[(1S)-1-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexen-1-yl]-3-methyl-2,4- pentadienoic acid, CAS RN: 21293-29-8]
- Ancymidol [alpha-cyclopropyl-α-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-pyrimidinemethanol, CAS RN: 12771-68-5]
- Butralin [4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N-(1-methylpropyl)-2,6-dinitrobenzenamine, CAS RN: 33629-47-9]
- Carbaryl [1-naphthalenyl methylcarbamate, CAS RN: 63-25-2]
- Chlorfluren [2-chloro-9H-fluorene-9-carboxylic acid, CAS RN: 24539-66-0]
- Chlorflurenol 2-chloro-9-hydroxy-9H-fluorene-9-carboxylic acid, CAS RN: 2464-37-1]
- Chlormequat 2-chloro-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium CAS RN.:7003-89-6
- Chlorpropham [1-methylethyl (3-chlorophenyl)carbamate, CAS RN: 101-21-3]
- Daminozide butanedioic acid mono(2,2-dimethylhydrazide) CAS RN.:1596-84-5
- Dichlorflurenol [2,7-dichloro-9-hydroxy-9H-fluorene-9-carboxylic acid, CAS RN: 69622-79-3]
- Dikegulac [2,3:4,6-bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-α-L-xylo-2-hexulofuranosonic acid, CAS RN: 18467-77-1]
- Flumetralin [2-chloro-N-[2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-ethyl-6- fluorobenzenemethanamine, CAS RN: 62924-70-3]
- Fluoridamid [N-[4-methyl-3-[[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]amino]phenyl]acetamide, CAS RN: 47000-92-0]
- Flurenol [9-hydroxy-9H-fluorene-9-carboxylic acid, CAS RN: 467-69-6]
- Flurprimidol alpha-(1-methylethyl)-α-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-5-pyrimidinemethanol CAS RN: 56425-91-3
- Fosamine [ethyl hydrogen (aminocarbonyl)phosphonate, CAS RN: 59682-52-9]
- Glyphosine [N,N-bis(phosphonomethyl)glycine, CAS RN: 2439-99-8]
- Isopyrimol [alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-α-(1-methylethyl)-5-pyrimidinemethanol, CAS RN: 55283-69-7]
- Jasmonic acid [(1R,2R)-3-oxo-2-(2Z)-2-pentenylcyclopentaneacetic acid, CAS RN: 6894-38-8]
- Maleic hydrazide [1,2-dihydro-3,6-pyridazinedione, CAS RN: 123-33-1]
- Mefluidide N-[2,4-dimethyl-5-[[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]amino]phenyl]acetamide CAS RN: 53780-34-0
- Mepiquat [1,1-dimethylpiperidinium, CAS RN: 15302-91-7]
- Piproctanyl [1-(3,7-dimethyloctyl)-1-(2-propenyl)piperidinium, CAS RN: 69309-47-3]
- Prohydrojasmon (±)-Propyl (1R,2R)-3-oxo-2-pentylcyclopentaneacetate, CAS RN: 158474-72-7]
- Propham [1-methylethyl phenylcarbamate, CAS RN: 122-42-9]
- Paclobutrazol (±)-(R',R')-beta-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-alpha-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1- ethanol CAS RN: 76738-62-0
- Tetcyclacis (±)-(3aR,4R,4aS,6aR,7R,7aS)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3a,4,4a,6a,7,7a- hexahydro-4,7-methano-1H-[1,2]diazeto[3,4-f] benzotriazole CAS RN: 77788-21-7
- 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid [CAS RN: 88-82-4]
- Uniconazole (betaE)-beta-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]-alpha-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4- triazole-1-ethanol CAS RN: 83657-22-1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PLANT HORMONE:
Auxin is one of five (or more) major plant hormones (Auxin, Cytokinins, Gibberellins, Ethylene and Abscisic acid) which affect numerous plant growth processes functions including cell division and elongation, autumnal loss of leaves, and the formation of buds, roots, flowers, and fruit. Auxin action is inhibited by light which is an important role of the growth of stems toward light (phototropism), against the force of gravity (geotropism) and positively hydrotropic (moisture-seeking). The cells exposed to light don't grow as quickly as those on the shaded side, and thus the plant grows toward the light source. Auxins usually have a ring system with at least one double bond and attached by a side-chain that terminates in a carboxyl group. Indole acetic acid is the exact structure of Auxin activity. Parent compounds of auxin action are;
- Auxins
- 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (CAS RN: 122-88-3)
- (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (CAS RN: 94-75-7)
- 4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (CAS RN: 94-82-6)
- Tris[2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)ethyl] phosphite (CAS RN: 94-84-8)
- 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 120-36-5)
- 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 93-72-1)
- Indole-3-acetic acid (CAS RN: 87-51-4)
- Indole-3-butyric acid (CAS RN: 133-32-4)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetamide (CAS RN: 86-86-2)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (CAS RN: 86-87-3)
- 1-Naphthol (CAS RN: 90-15-3)
- Naphthoxy acetic acid (CAS RN: 120-23-0)
- Naphthenic acid, inorganic salts (potassium, sodium)
- (2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy) Acetic acid (CAS RN: 93-76-5)
- Antiauxins
- Clofibric acid (CAS RN: 882-09-7)
- 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid (CAS RN: 88-82-4)
Cytokinin is a N6-substituted adenines acting as phytohormones such as kinetin, zeatin, 6-isopentenyladenine, benzyl adenine. The principal functions are stimulate cell division in concert with auxin (cytokinesis) and influence the pathway of tissue differentiation (organogenesis). 6-Benzylaminopurine is the first generation synthetic cytokinin which elicits plant growth and development responses setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. Active cytokinin ingredients include:
- Adenine (CAS RN: 73-24-5)
- Adenine Hemisulfate salt (CAS RN: 321-30-2)
- 6-Benzylaminopurine (CAS RN: 1214-39-7(base), 162714-86-5(HCl)
- N-Benzyl-9-(2-tetrahydropyranyl)adenine (CAS RN: 2312-73-4)
- N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N'-phenylurea (CAS RN: 68157-60-8)
- 6-(gamma,gamma-Dimethylallylamino)purine (CAS RN: 2365-40-4)
- 1,3-Diphenylurea (CAS RN: 102-07-8)
- Kinetin (CAS RN: 525-79-1 (base), 177966-68-6 (HCl)
- 1-Phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl) Urea (CAS RN: 51707-55-2)
- Zeatin (CAS RN: 13114-27-7)
- trans-Zeatin (CAS RN: 1637-39-4 (base), 6025-81-6 (HCl))
- trans-Zeatin riboside (CAS RN: 6025-53-2)
Other Plant Growth Regulators include:
- Abscisic acid (CAS RN: 21293-29-8)
- Ancymidol (CAS RN: 12771-68-5)
- Chlorocholine chloride (CAS RN: 999-81-5)
- Daminozide (CAS RN: 1596-84-5)
- 3,6-Dichloro-o-anisic acid (CAS RN: 1918-00-9)
- Gibberellic acid (CAS RN: 77-06-5)
- Gibberellic acid Potassium salt (CAS RN: 125-67-7)
- Gibberellin A4 (CAS RN: 468-44-0 ) and other gibberellins (more than 110 gibberellins are known)
- Glyphosate (CAS RN: 1071-83-6)
- Jasmonic acid (CAS RN: 3572-66-5)
- 1,3,5-Trihydroxybenzene (CAS RN: 108-73-6)
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min
Not
a dangerous substance according to GHS
Hazard
Symbols: , Risk Phrases: ,
Safety
Phrase: 22-24/25