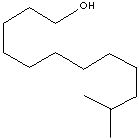
| ISOTRIDECANOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 27458-92-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 248-469-2 | |
| FORMULA | C13H28O | |
| MOL WT. | 200.36 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Isotridecan-1-ol; Isotridécane-1-ol; | |
| Mixture of branched C13 linear alcohols; | ||
|
SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
clear liquid |
|
| MELTING POINT | < -30 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 245 - 255 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.84 - 0.85 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | 6.9 | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
130 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions, | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Isotridecanol is a branched, linear and primary alcohol with high mole wt. It is a used as a raw material in the industries of cosmetics, drug delivery, metal processing, fiber finish, thermostable and biodegradable lubricant and solvent as well as surfactant. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid |
|
|
CONTENT |
97.0% min |
|
|
ACID NUMBER |
0.1 max (mg KOH/g) |
|
|
COLOR, APHA |
20 max |
|
|
HYDROXYL NUMBER |
275 min (mg KOH/g) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 160kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FATTY ALCOHOL |
||
Fatty alcohols, derived from natural fats and oils, are high molecular straight
chain primary alcohols. They include lauryl (C12), MyrIstyl (C14), Cetyl ( or
palmityl: C16), stearyl (C18), Oleyl (C18, unsaturated), and Linoleyl (C18,
polyunsaturated) alcohols. There are synthetic fatty alcohols equivalent
physically and chemically to natural alcohols obtained from oleochemical sources
such as coconut and palm kernel oil. Fatty alcohols are emulsifiers and
emollients to make skin smoother and prevent moisture loss. Identical fatty
esters are used to improve rub-out of formulas and to control viscosity and
dispersion characteristics in cosmetics, personal care products and
pharmaceutical ingredients. As chemical intermediates, the primary use of fatty
alcohols are as raw material for the production of fatty sulfate salts and
alcohol ethoxylates for foaming and cleaning purposes in the field of detergent
industry. Chemical reactions of primary alcohols include esterifications,
ethoxylation, sulfation, oxidation and many other reactions. Their derivatives
and end use applications include;
Large amount of fatty alcohols are used as special solvents, fillers in plasticizer and insulating materials for the building industry. Fatty alcohols are used as ingredients in the industries of agricultural, foodstuff, metal processing, cosmetics, lube additive, pharmaceutical, rubber, textile, perfume and flavouring as well as synthetic detergent. |
||