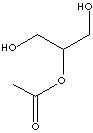
| MONOACETIN
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 26446-35-5 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 247-704-6 | |
| FORMULA | C5H10O4 | |
| MOL WT. | 134.13 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2915.39 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS |
1,2,3-Propanetriol, Monoacetate; |
|
|
Acetyl Monoglyceride; Glycerin Monoacetate; 1-Monoacetin; Acetin; Glycerol, 1-Acetate; alpha-Monoacetin; Glycerol Monoacetate; glycerol alpha-monoacetate; glycerol monoacetate; Glyceryl Acetate; Glyceryl Monoacetate; Monoacetyl Glycerine; |
||
| SMILES |
glycerol with strong acetic acid |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear oily liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.21 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
soluble |
|
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| HENRY'S LAW |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | > 110 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Triacetin, triacetate ester of glycerol, is a clear, combustible and oily liquid with a bitter taste and a fatty odor. It is slightly soluble in water but soluble in alcohol and ether. It has properties of both glycerol and acetate. Diacetin (CAS RN: 25395-31-7) and nonoacetin (CAS RN: 26446-35-5) are glycerin diacetate and glycerin monoacetate respectively. Triacetin is found in some food like butter as it is used as a food additive for the solvency of flavourings for the function of humectant. It is used in perfumery and cosmetics for these applications. It is used as an antifungal agent in external medicine for topical treatment of superficial fungal infections of the skin. Triacetin is applied to cigarette filter as a plasticizer. It is used as a gelatinizing agent in explosives. Monoacetin is used as a solvent, plasticizer and softening agent. It is used as a food additive, solvent for dyes. It is used in manufacturing explosives and smokeless powder. It is used in leather tanning. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear oily liquid | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
| ACIDITY | 0.01% max | |
|
COLOR , APHA |
10 max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 240kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| European Hazard Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF GLYCEROL | ||
Glycerine (glycerin, glycerol, or 1,2,3-propanetriol) is the simplest trihedric alcohol. Pure glycerine, with a specific gravity of 1.26, is a colorless, odorless, sweet, viscous liquid melting at 17.8 C boiling at 290 C. It decomposes at boiling point and produce corrosive fumes of acrolein. It is miscible in water and forms a solution in any proportion. It is also soluble alcohol but only partially soluble in common organic solvents such as ether and ethyl acetate. It resists freezing. It is hygroscopic, which favors as a humectant to retain moisture in cosmetics. It reacts violently with acetic anhydrides in the presence of a catalyst. It is obtained as a byproduct when fats and oils are hydrolyzed to yield fatty acids or soaps. Glycerol is also commercially synthesized from propylene (Dow Chemical). Glycerol can also be obtained based on a proprietary fermentation processing. Glycerol is widely used; as a solvent, food additive, sweetening agent and emollient and emulcent with magnesium sulphate used in the treatment of septic wounds and boils; in the manufacture of alkyd resin, cellophane, ester gums, plasticizer, dynamite, nitroglycerine, cosmetics, liquid soap, perfume and toothpaste (good solubility and taste give glycerine an edge on sorbitol in toothpastes, which are estimated to make up almost one-third of glycerine's market in personal care products); as a component of antifreeze mixtures; to keep fabrics pliable, to preserve printing on cotton, to keep frost from windshields; as a source of nutrients for fermentation cultures in the production of antibiotics; as a preservative in some pharmaceutical and biological preparations and in non-alcoholic extracts and tinctures. It has many other applications. |
||