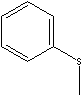
| THIOANISOLE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 100-68-5 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 202-878-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C6H5SCH3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 124.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE |
2930.90.2900 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Rat LD50 (Oral): 891mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Methyl phenyl sulfide; (Methylthio)benzene; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl phenyl sulphide; Sulfuro de fenilo y metilo; Sulfure de méthyle et de phényle; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
c1(ccccc1)SC |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Thioether, Flavor and Fragrance agent, Sulfide |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear to yellowish liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | -15 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 188 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 506 mg/l at 25 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | soluble in most common organic solvents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| log Pow | 2.74 (Octanol-water) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HENRY'S LAW | 1.57E-04 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OH RATE | 1.36E-11 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.585 - 1.587 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | 57 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sulfoxide (R2SO) is any of various organic sulfur compounds having the group -SO (sulfinyl group) whereas sulfone (RSOOR) with the group -SO2 (sulfonyl group). They are derived from oxidation of sulfides ((R-S-R). Thioethers (organic sulfides) can be oxidized either to oxidation state -1 disulfides (R-S-S-R) or to oxidation state 0 sulfoxides (R-S(=O)-R) which can be further oxidized to the corresponding oxidation state +2 sulfones (R-S(=O)2-R) depending on the structure of the thioether. They are widely used as solvent of both extraction and reaction as well as intermediates for the synthesis of textile chemicals and pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Thioether is the sulfur analog of the ether (R-O-R), which sulfur atom replaces the oxygen. Sulfur and oxygen belong to the same group in the periodic table share similar chemical properties. The functional groups of sulfur and oxygen share similar chemical bonds and properties. Ethers can only be oxidized to peroxides (R-O-O-R). But thioethers (R-S-R) can be oxidized either to disulfides (R-S-S-R) or to sulfoxides (R-S(=O)-R) which can be further oxidized to the corresponding sulfones (R-S(=O)2-R) depending on the structure of the thioether. Dimethyl Sulfide is the simplest thioether. The compound is a clear, flammable liquid; insoluble in water; boiling point 37C; with a distinctive garlic-like odor. It is used as a flavor component to enhance corn-related flavors. It is used as a presulfiding agent in the refinery and petrochemical production. The catalysts in hydrocracking, hydrodenitrification, hydrodesulfurization and reforming processes are used in oxide forms, which must be converted to the active sulfide form during the start-up to prevent the reduction of the catalysts to their base material by heat. The sulfur sources include alkyl mercaptans (methyl mercaptan, ethyl mercaptan, butyl mercaptan), dimethyl sulfide, dimethyl sulfoxide, dimethyl disulfide, and tert-nolyl polysulfide. They are used to modify the reactivity of catalysts to use in high temperature process furnaces. Dimethyl Sulfide is used to prevent the coke deposits which acts as a thermal insulator in the tube as it accumulates in pyrolysis furnaces. It is also used in steel mill furnaces to control dusting. Dimethyl Sulfide is included as a component of dangerous gases to detect the leaks by smell. Thioethers have applications in organic synthesis as solvents as well as reagents. Acyclic thioethers with oxidized branches such as alcohol, aldehyde, ester, acid, beta-ketone, phenol demonstrate centres of greater polarity and additional functional sites for the additional uses. Cyclic sulfides containing oxidized carbon atoms would involve extensive S-oxidation. Thioethers are involved in versatile in the synthesis of specific compound classes include agricultural chemical, property-enhancing additives, pharmacological drugs, chemical resistant polymers, detergents, and rubber antioxidants. Some examples of aliphatic and aromatic thioethers found in flavouring agents include:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to yellowish liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
0.5% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 3 (Packing Group: III) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 1993 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 24/25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||