| OXALYL BROMIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 15219-34-8 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 239-271-7 | |
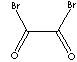
| FORMULA | BrCOCOBr | |
| MOL WT. | 215.83 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2917.19 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Ethandioyl Bromide; Ethanedioyl Divromide; | |
| Oxalic dibromide; Oxaloyl bromide; Oxalyl Dibromide; | ||
|
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT |
-19 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 105 - 107 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Reacts (soluble in ether, benzene, chloroform) | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 1 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Oxalic Acid (also called Ethanedioic Acid) is a colourless, crystalline, toxic organic compound belonging to the family of dicarboxylic acids; melting at 187 C; soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. It occurs in the form of its metal salts (usually calcium or potassium) in many plants. It is commercially manufactured by heating sodium formate in the presence of an alkali catalyst to form sodium oxalate, which should be converted to free oxalic acid when treated with sulfuric acid. It is also prepared by oxidizing carbohydrates with nitric acid, by heating saw dust with caustic alkalies or by fermentation of sugar solutions in the presence of certain molds. Oxalic acid is the only possible compound in which two carboxyl groups are joined directly; for this reason oxalic acid is one of the strongest acids in organic compounds. Unlike other carboxylic acids, oxalic acid (and formic acid) is readily oxidized and combine with calcium, iron, sodium, magnesium, or potassium to form less soluble salts called oxalates. Oxalic acid and oxalates are useful as reducing agents for photography, bleaching, and rust removal. They are widely used as an purifying agent in pharmaceutical industry, precipitating agent in rare-earth metal processing, bleaching agent in textile and wood industry, rust-remover for metal treatment, grinding agent, waste water treatment. acid rinse in laundries and removing scale from automobile radiators. The electronegative atom presence tends to strengthen the acidic property. Oxalyl Bromide which has two alpha-carbons in the smallest chain is used as a brominating agent in organic synthesis. The strong acid releases the stable conjugate base (halide anion except F) with small strength differences of Cl- < Br- < I-. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
| PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
| BOILING POINT | 105 - 107 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 250kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 1760 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34, Safety Phrases: 25-36/37/39-45 | ||