| METHYL ACETOACETATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 105-45-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-299-8 | |
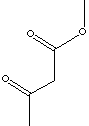
| FORMULA | CH3COCH2COOCH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 116.12 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2918.30 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 3228 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Methyl 3-ketobutyrate; Methyl acetylacetate; | |
| Methyl 3-oxobutanoate; Methyl 3-oxobutyrate; Acetoacetic acid methyl ester; Methyl acetonecarboxylate; Methylacetoacetat (German); acetoacetato de metilo (Spanish); acétoacétate de méthyle (French); | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid,fruity odor | |
| MELTING POINT | -30 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 169 - 170 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.08 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble (completely soluble in alcohol and ether) | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 67 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Acetoacetone is a beta-diketone (1,3-diketone) which two ketones are separated only by one carbon. The beta-ketone is stable as a conjugated enol rather than alpha-diketone due to the delocalization which makes the counterion more stable and less likely to regain the proton. Ascorbic acid is an example of enol compound. Enol compounds form complexes with many transition metal ions. These compounds are readily soluble in organic solvents. They are widely used as chelating agents, ligands, and catalyst precursors. Acetoacetic acid and its esters contain active methylene groups which have relatively acidic alpha-protons due to H atom adjacent to two carbonyl groups. The reactivity of its methylene group provide the sequence of reactions of alkylation, hydrolysis of the esters and decarboxylation resulting in substituted ketones. The methylene group can be reacted to form amino-carbonyl compounds. Acetoacetates are important aliphatic parts adjoining azo dyes and pigments. Acetoacetic acid is unstable and decompose to acetone and carbon dioxide at room temperature. Aacetoacetate is one of ketone bodies which are the end-products of rapid or excessive fatty acid breakdown in the human body. Methyl acetoacetate has a reactive hydrogen atom on the carbon alpha to both carbonyl groups. It undergoes Knoevenagel condensation reaction as a reactant to forms a large class of target products including amino acids, drugs, colorants, lacquers, perfumes, and plastics. Alone, it is used as a flavoring agent and a solvent. Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of a reactive hydrogen atom at 1,3-diketone compounds to a carbonyl group, followed by an dehydration reaction. 1,3-Diketone compounds (beta-ketones) include malonic acid, diethyl malonate, Meldrum's acid, and acetoacetic acid derivatives. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
|
PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.07 - 1.08 | |
|
WATER |
0.3% max |
|
|
COLOR, APHA |
10 max | |
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36, Safety Phrases: 26 | ||