PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
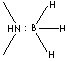
(CH3)2NH:BH3
TOXICITY
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.73
8 - 9 (10%)
REFRACTIVE INDEX
43 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Application:
Reagent used in a Ni-catalyzed reduction of electron-deficient aryl
tosylates.1 The catalyst is composed of commercially available
Ni(PPh3)2Cl2(529621) and PCy3
Local:
Application:
- Deprotection of Cbz group catalyzed by nickel complexes.
- Reduction of Non-basic reagent, not acid-sensitive (aldehyde, ketone to alcohol )
- Mild and selective reduction catalyzed by nickel complexes. (aryl halide to arene)
- Aromatic aldehydes and ketones deoxygenated in the presence of TiCl4. (Rreduction of carbonyl to alkane)
Borane (boron hydride): any binary compound of boron and hydrogen. The term borane describe sometimes denote substances considered to be derivatives of the boron-hydrogen compounds, such as BCl3 and B10H12I2. Borane can be made from magnesium boride (MgB2) with the action of acid or can be prepared by the breaking apart of complex molecules into simpler products on heating in the presence of hydrogen. Boranes form interesting structures which cannot be described by the conventional two-electron covalent bond model. There are fewer electrons forming the chemical bonds than required in normal electron-pair bonds. An electron pair bonds both boron and the bridging hydrogen atom to create three atoms bond. There are two major general formula system; BnHn+4 (nidoboranes) and BnHn+6 (arachnoboranes). The simplest is diborane (B2H6), highly reactive gas; used as a rocket fuel and in hydroboration process to prepare organoboranes which have application as intermediates for organic synthesis. Boranes are all reactive and oxidize readily in air. There is a wide range of boranes with shapes ranging from delicate spiders' webs to untidy birds' nests. There is also a wide range of borane derivatives containing other atoms, such as carbon and phosphorus. Carborane is a class of stable cluster compounds containing carbon, boron and hydrogen external to the framework of the cluster; with general formula C2BnHn+2. Carborane bonds are non-classical but have thermal stability and neutron capture ability, when containing the 10B isotope. A cluster compound is one with insufficient electrons to allow for classical two-center two-electron bonds between all adjacent atoms. Boranes including borane (BH3), borobutane (B4H10), and borodecane (B10H14) are used as fuels for air breathing engines and rockets as thery have higher calorific values than hydroborons fuels, once proposed as high-energy fuels for aircraft and missiles. Boranes are used in the synthesis of other organic boron compounds and metal borohydrides. They are used as chemo- or stereo-selective reductants. They convert aldehydes (chemoselective), ketones (stereoselective) to the corresponding alcohols in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals. They are used in the reductive alkylation of amines, novel metals and oximes. They are used as polymerization initiators (especially Trialkylboranes) for many monomers. They are used in extracting metals (Ag, Pd, Au, Ni). Applications include metal coatings, fogging agents in photographic emulsions, polymer additives and nitride-boron coatings.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
PRICE INFORMATION