|
CHLOROFORM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. |
67-66-3 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 200-663-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
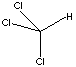
| FORMULA | CHCl3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 119.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2903.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
oral rat LD50: 910 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Trichloromethane; Methyl Trichloride; Formyl Trichloride; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methane Trichloride; Methenyl Trichloride; Trichloroform; Chloroforme (French); Cloroformio (Italian); Trichloormethaan (Dutch); Trichlormethan (Czech); Triclorometano (Italian); | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
Methyl chloride with Chlorine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear volatilie liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | -63.5 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 61 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.492 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Slightly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 4.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4460 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0 ; Reactivity: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | practically not flammable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Chloroform, trichlorinated methane, is a clear, colorless, sweat smelling, heavy and volatile liquid haloform. Other haloforms are fluoroform, CHF3, bromoform, CHBr3, and iodoform, CHI3. It is slightly soluble in water and is miscible with ethanol, ether, and other organic solvents. Chloroform is produced by direct heating of methyl chloride with chlorine to 500 C. This heating process produces spontaneously a series of chloromethanes, chloromethane, dichloromethane, trichloromethane(chloroform), and tetrachloromethane which are then separated by distillation. Chloroform is broken down to phosgene, hydrochloric acid, and chlorine upon exposure to air, light, and heat. This compound violently reacts with acetone in the presence of potassium hydroxide or strong caustics. It may react explosively with fluorine, N2O4, and methanol. It may also react explosively with chemically active metals such as aluminum, lithium sodium, or potassium. It will attack some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings. Chloroform was an effective anaesthetic but can cause carcinogenic effects. It has been replaced entirely by other less toxic, more easily controlled halogenated hydrocarbons. It is used primarily in the manufacture of chlorofluorocarbon, CFC-22. Chloroform reacts with a strong base (sodium hydroxide) to form dichlorocarbene in the presence of a phase transfer catalysts. This is an reactive intermediate during organic synthesis and effects in very different forms. It is a major raw material in the production of plastics, especially vinyl chloride. It is also used as an industrial solvent for lacquers, resins, rubber, fats, greases, gums, waxes, adhesives, oils, and dry cleaning. It is a useful heat transfer medium in fire extinguishers. Other uses include fumigants, insecticides, manufacture of anesthetics and pharmaceuticals, primary source for chlorodifluoromethane and many other chemical compounds. It is sometimes used as a biocide in preventing public disease as chlorination is effective to kill almost all bacteria and viruses. But this compound has been prohibited by the FDA to use in drugs, cosmetics and food packaging, cough medicines and toothpastes and etc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear volatilie liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PURITY |
99.9% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COLOR, AHHA |
10 max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACIDITY |
10ppm max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOISTURE |
100ppm max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 250kgs in drum, Iso-Tank | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing group : III) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 1888 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22-38-40-48/20/22, Safety Phrases: 36/37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CHLORINATED SOLVENTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The production and use of 1,1,1-trichloroethane and carbon tetrachloride have been phased out throughout the world because of suspected harm to the earth's ozone layer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||