| COBALT OXIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1307-96-6
(Divalent), 1308-04-9 (Trivalent), 1308-06-1 (II, III) |
|
| EINECS NO. |
215-154-6
(Divalent), 215-157-2 (II, III) | |
| FORMULA | CoO, Co2O3, Co3O4 | |
| MOL WT. | 74.93, 165.86, 240.80 | |
|
H.S.CODE |
| |
| TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50:
202 mg/kg (Divalent), Oral rat LD50: >5000 mg/kg (II, III) | |
| SYNONYMS | Cobalto-cobaltic oxide; Co3O4; Cobalt(II, III) oxide; | |
| Cobaltic-cobaltous oxide; Cobaltosic oxide; Tricobalt tetraoxide; | ||
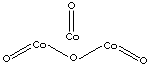
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Black-gray crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 895 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | 3800 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 6.11 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Cobalt is a lustrous, silvery-blue metallic chemical element, symbol Co, atomic number of 27 and an atomic weight of 58.93. Cobalt is obtained primarily as a by-product of the mining and processing of copper and nickel ores. Examples of cobalt ores include cobaltite [(Co,Fe)AsS], erythrite [(Co3(AsO4)2·8H2O)]. fukuchilite ( Cu3FeS8), glaucodot [(Co,Fe)AsS], linnaeite [(Co,Ni)3S4], skutterudite [(Co,Ni,Fe)As3], and smaltite [(Co,Fe,Ni)As2]. Cobalt is extracted as a by-product of nickel and copper concentration through pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical and electrolytic processes. Cobalt contributes corrosion resistant and hardness if alloyed with other metals and when used in electroplating. The major uses of cobalt is preparing metal alloys. Cobalt-60 with a half-life of 5.3 years is a gamma ray source when used in radiotherapy and sterilization. It is used as a catalyst in the petroleum production and chemical synthesis. Cobalt-molybdate catalyst is active in desulfurization of petroleum. Cobalt is combined with many other elements including chlorine, sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen. In addition to a common state +1, the most prevalent oxidation states of cobalt are +2 and +3. Cobalt compounds are used as pigments in glass and ceramics. It is used as a drying agent for paints, varnishes and inks. Cobalt sulfate is any sulfate salt of either divalent or trivalent cobalt. Divalent cobalt sulfate anhydrous (CoSO4) melts at 96.8 C; soluble in methanol. It is used in preparing pigments and other cobalt salts. Trivalent cobalt sulfate [called cobaltic sulfate, Co2(SO4)3] contains trivalent cobalt acts as an oxidizing agent; soluble in sulfuric acid. Cobalt pigment is used in porcelains and glass. Cobalt sulfate is used in storage batteries and electroplating baths. It is used in sympathetic inks and as an additive to soils and animal feeds. It is a raw material to make other cobalt salts. Cobalt oxide is a metallic pigment that provides blue coloring in porcelains and glass. Various forms of cobalt oxide are changes to CoO at 850 - 900 C. CoO is a grayish brown powder that decomposes at 1935 C, insoluble in water. It is also used as a drying agent in inks and varnishes and as a feed and fertilizer additive. Cobalt carbonate has same coloring application as it decomposes to cobalt oxide at high temperature. Cobalt carbonate tends to disperse better in a glaze but can produce blisters because of the CO2 gas presence at high temperature. Commercial grades of cobalt carbonate are the complex of carbonate and hydroxide such as cobalt carbonate hydroxide (1:1) (CAS RN: 12069-68-0), Cobalt carbonate hydroxide (2:3) (CAS RN: 12602-23-2), and cobalt carbonate hydroxide (2:3) monohydrate (CAS RN: 51839-24-8). |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Black-gray crystalline powder | |
| Co | 71.0% min | |
|
Fe |
0.001% max | |
|
Ni |
0.03% max | |
| Mn | 0.03% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgd in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
| |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN N, Risk Phrases: 22-43-50/53, Safety Phrases: 22-24-37-60-61 | ||
|
PRICES |
||